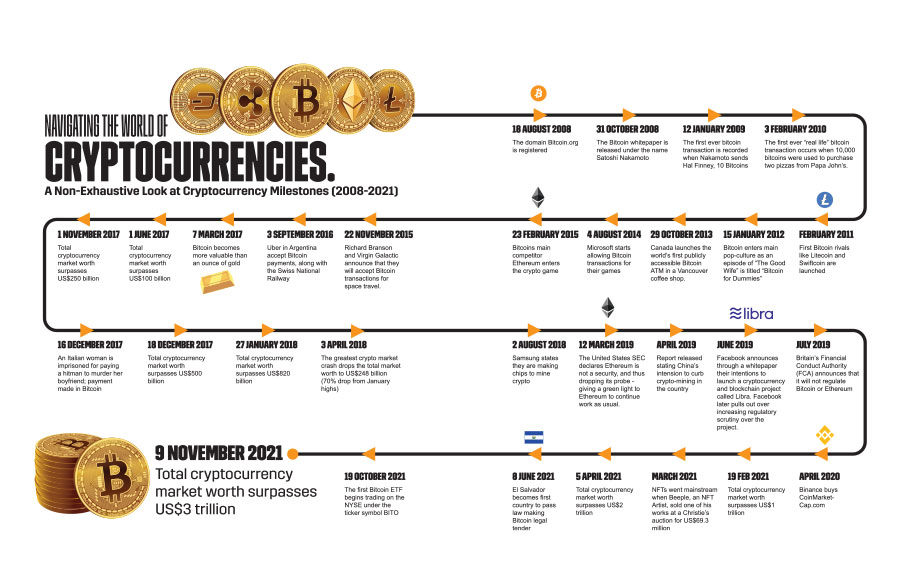
Navigating the World of Cryptocurrencies
03 June 2022•
There are many digital or cryptocurrencies, not dozens, or hundreds but over ten thousand digital currencies. Bitcoin is the main one, which comprises roughly 40% of the total crypto market value. All others are Altcoins, of which there are over 10,000 and new altcoins are being launched daily.
Bitcoin (BTC): The First Cryptocurrency Ever Invented.
Bitcoin, also known as BTC, is the world’s first ever cryptocurrency, and it just so happens to also be the world’s most valuable cryptocurrency, commanding roughly 40% of the total crypto market value. Bitcoin was revolutionary because it was the first decentralized digital currency that eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks and governments, using instead a peer-to-peer computer network to confirm purchases directly between users.
So how does it work? Bitcoin is powered by an open-source code or technology known as the blockchain. Blockchain is a technology that creates a shared public ledger of transactions organized into “blocks” that are time-stamped and “chained” together to prevent any kind of tampering. The blockchain is an incredibly secure record-keeping technology that allows strangers to put trust into exchanging Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies online. Members of the global peer-to-peer computer network independently confirm transactions using high-speed computers, typically within 10 to 20 minutes; these members are known as Bitcoin Miners.
These miners are paid in Bitcoin to reward their efforts, which incentivizes the network to continue to independently verify each transaction. These Bitcoin Miners are essential to the blockchain working, as this network of independent miners are required to confirm the authenticity of each block of data before it’s added to the blockchain, in a process known as “proof-of-work”.
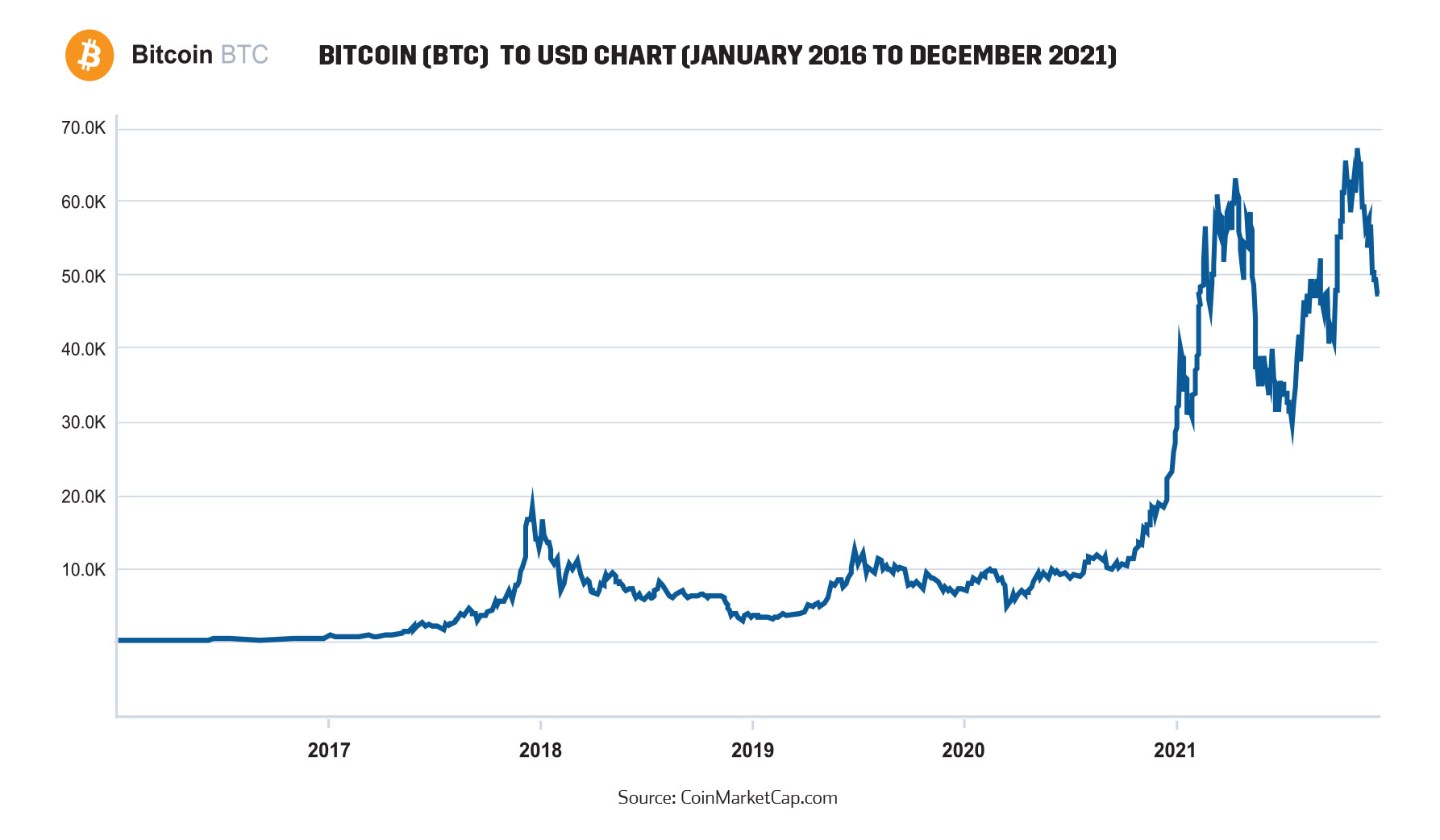
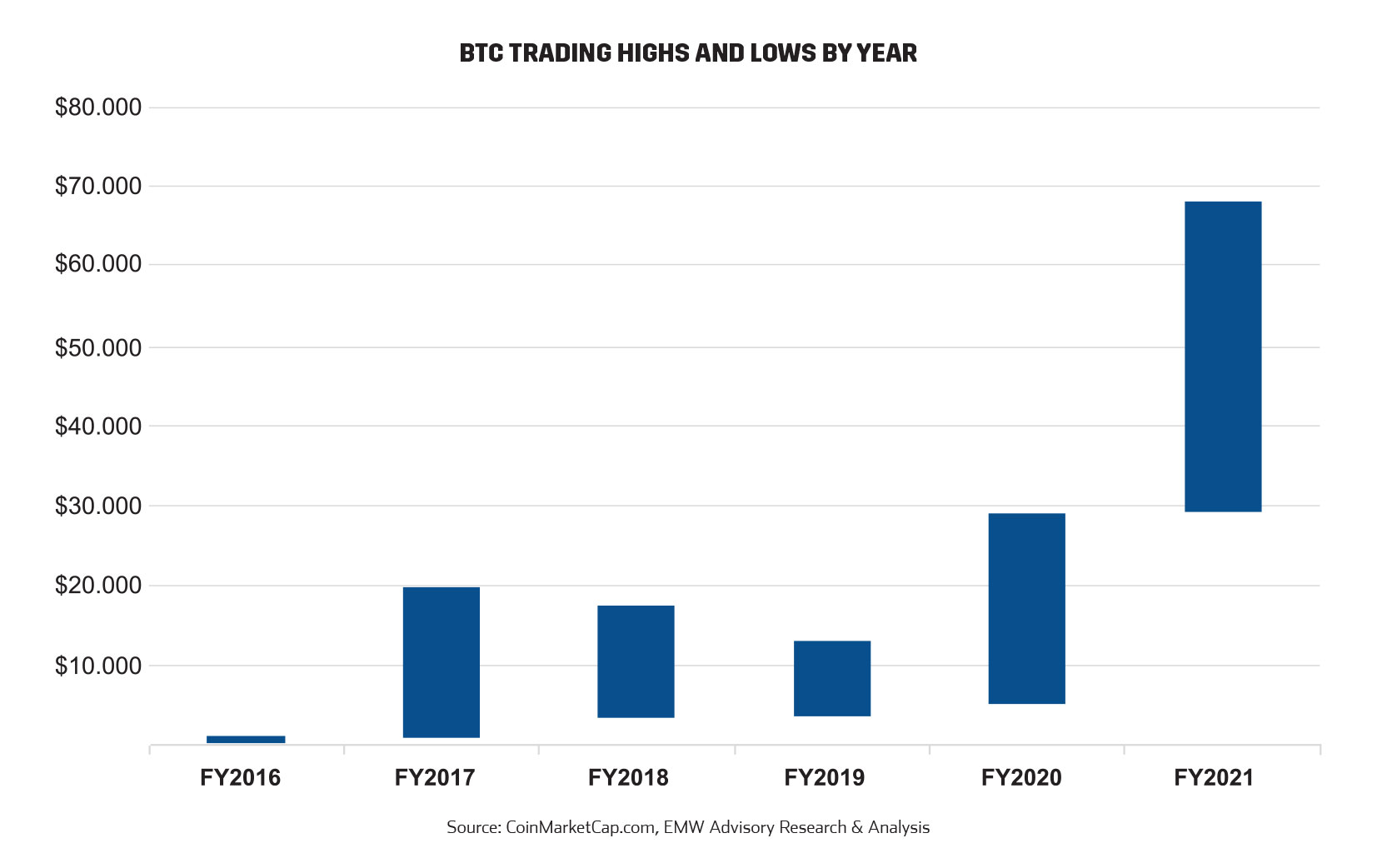
Bitcoin (BTC) has grown from a fringe experiment in decentralized finance (DeFi), to becoming many investors’ golden “get-rich-quick” ticket – making overnight millionaires by the thousands. At its’ height in November 2021, the combined value of all Bitcoins (BTC) was more than US $1 trillion, exceeding market capitalizations of some of the world’s largest companies including Tesla, Berkshire Hathaway and Facebook parent Meta. In February 2021, when the price of Bitcoin grew to over US$57,000, it was estimated that there were 100,000 bitcoin millionaires. One year prior, there were only 15,000 millionaire Bitcoin accounts11.
Definitions:
Open-Source Code: refers to code that is designed to be publicly accessible – anyone can see, modify, and distribute the code as they see fit. Open-source software is developed in a decentralized and collaborative way, relying on peer review and community collaboration.
Blockchain: is a technology that creates a shared public ledger of transactions organized into “blocks” that are time-stamped and “chained” together to prevent tampering.
Bitcoin Mining: is the process in which new transactions are confirmed on the blockchain and a critical component of the maintenance and development of the blockchain ledger. Bitcoin Miners compete with each other to be the first to complete auditing the ledger; the winning miner gets rewarded in Bitcoin. Mining is also the only method in which new bitcoins are entered into circulation. Bitcoin mining requires energy-intensive and sophisticated hardware that solves extremely complex computational math problems.
Proof-of-Work (PoW): is what miners work to accomplish when cryptocurrency mining; in essence, PoW is a decentralized consensus mechanism that requires members of the network to expend effort solving an arbitrary mathematical puzzle to prevent anybody from gaming the system. Proof of Work is used widely in cryptocurrency mining, for validating transactions and mining new tokens.
But how are people making money off Bitcoin (BTC) and why is it so volatile? At its essence, Bitcoin value follows the laws of supply and demand – and because there is a limited supply of Bitcoins – there are currently 18.9 million Bitcoin in circulation, 90% out of a maximum threshold of 21 million12(by Nakamoto’s design) – this market inelasticity is one of the reasons why analysts believe the price of Bitcoin has and will remain volatile. Because there is no central bank that can artificially subdue volatility or intervene, Bitcoin’s volatility is proof of a distortion-free market. It is exactly because of this volatility, that investors (with nerves of steel) are making money. After all, where there is great risk, there is the potential for great reward. Most people that are purchasing Bitcoin (or Altcoins for that matter) are doing so as a form of currency speculation; it is not dissimilar to picking stocks on the stock market or currency trading online; everyone who buys Bitcoin (and Altcoins) are hopeful that the value will increase over time.
Altcoins: Over Ten Thousand Alternatives to Bitcoin.

Altcoins, by definition, are any other digital currencies that are not the original Bitcoin. At the end of 2021 there are well over 10,000 alternative digital coins you can invest and trade in. Why are there so many alternatives to Bitcoin? There are many altcoins that have adopted the same DeFi premise as Bitcoin, but are using their coins to achieve different goals, or seek to improve a perceived flaw in Bitcoin or Bitcoin’s blockchain. Some altcoins have promised to be faster, more decentralized, more scalable, and/or more secure than Bitcoin, resulting in a dizzying ecosystem of altcoins.
There are 4 large buckets you can segment Altcoins into:
Native Cryptocurrencies
Tokens
Stablecoins
Forks
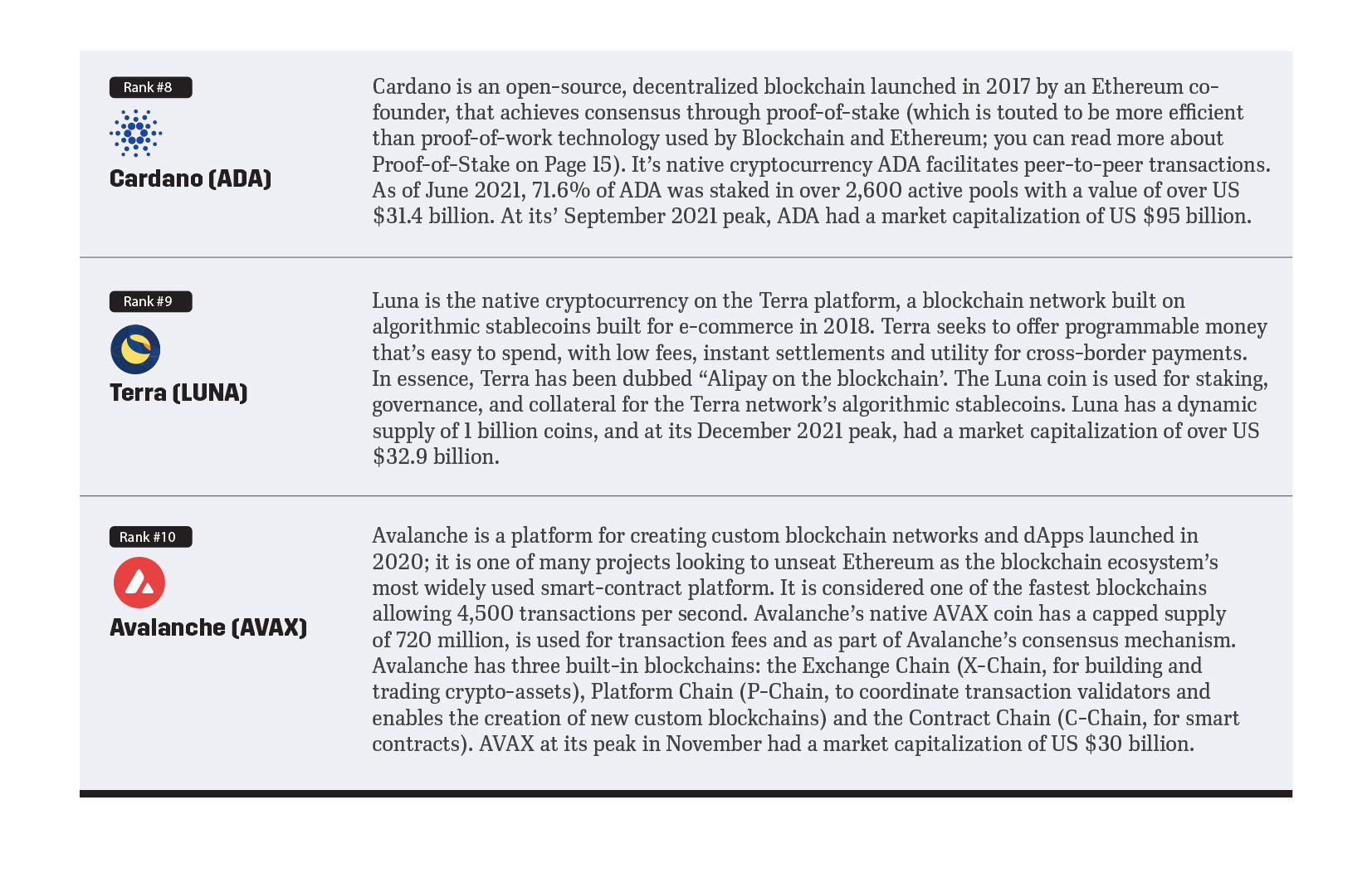
1. Native Cryptocurrencies: are coins that were originally created to run on their own specific blockchain network or ledger system. The top 3 cryptoassets by market capitalization are all native cryptocurrencies.
Eight of the Top 10 cryptocurrencies by market capitalization are native cryptocurrencies. The most common and most valuable examples of native cryptocurrencies are as follows:

2. Tokens: are a unit of value that operates on an already existing blockchain that has a utility specific to that token.
It is similar to buying arcade tokens with cash (fiat currency), specific to those games. A good analogy might be an arcade that specializes in pinball machines that may ask for a specific “pin-ball machine arcade token” to play. While another gaming arcade down the street may ask you to purchase their own arcade token to play their games. Tokens have no outside value, except for the utility in which they have been created. Some examples of Tokens include:


3. Stablecoins: were developed to peg cryptocurrencies to fiat currencies, in order to remove the price volatility inherent with other cryptocurrencies and tokens. Stablecoins don’t earn any profit for holders as their value remains consistent – but there are plenty of use cases for a coin that doesn’t gain or lose value by the minute. Stablecoins are good for exchange and storing value. For example, stablecoins are a good alternative to holding funds on a crypto exchange, instead of converting to US dollars. Stablecoins are also a good medium for sending and receiving funds globally. The advantage of holding stablecoins instead of US dollars when trading crypto is the transaction speed and significantly reduced transaction fees.
The fastest growing use of stablecoins are DeFi platforms, where users lend stablecoins to others to earn interest, without the involvement of an intermediary banking institution. Many cryptocurrency exchanges are offering free conversions from fiat currencies like US dollars into stablecoins like USD Tether (USDT) or USD coin (USDC), after which users will earn interest anywhere between 0.15% APY to 14% APY depending on the exchange. There are stablecoins that are pegged against all major currencies such as the US Dollar, Japanese Yen, Euro, and British Pound. Two of the most valuable stablecoins in the crypto-verse by market capitalization are:


4. Forks: are when a blockchain splits into a new blockchain following new set of protocols. When a group decides it wants to change the rules of one blockchain, it can validate and split the chain, and a new chain emerges ready to start logging transactions under the new rules agreed upon by those who chose to validate the fork. The original blockchain continues as normal. Forks can happen over and over and over again, creating new blockchains and cryptocurrencies along with it. Bitcoin cash is a fork of the original Bitcoin blockchain. Ethereum Classic is a fork of the original Ethereum system. Dogecoin is a fork of Luckycoin, which in turn was a fork of Litecoin, which was a fork of Bitcoin. To date, there have been over 100 BTC forks, of which approximately 70-75% have survived and are still functional.
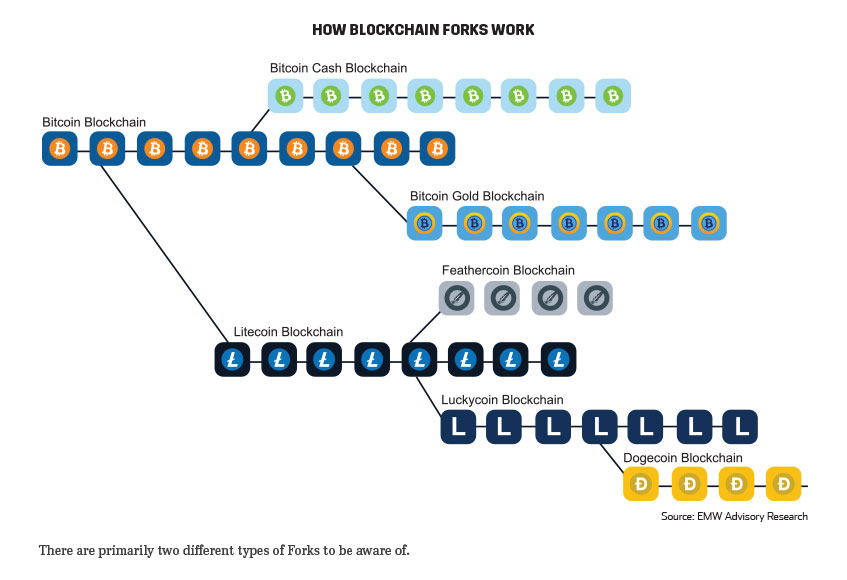
There are primarily two different types of Forks to be aware of.

Making Money in the Crypto-verse:
There are several key means to make money in the crypto-verse.
1. Investing and Trading cryptocurrencies and crypto assets. Most people you know who are “in Crypto” are investing in cryptocurrencies (either Bitcoin or Alt-Coins) and participating in cryptocurrency speculation. Like the general stock markets around the world, the objective of the game is to “Buy Low, and Sell High”. For day-traders, though the volatility of the cryptocurrency market is very high compared to traditional markets (read high volatility as high risk), high rewards can also be found within volatile markets. That said, crypto assets have tremendous long-term potential for growth; thus are well-suited to a “buy-and-hold” strategy. Most investors agree though: invest money you’re willing to place and forget about for while; and don’t invest anything you’re not willing to lose – as “crypto winters” tend to last years, not months – and there’s always a risk that your bet, wasn’t the right bet. If you’re interested in investing and trading in crypto, you will also have to consider what platform(s) you will sign-on to. Different trading platforms have different transaction or ‘gas’ fees, which can vary significantly. Different trading platforms also sell varied alt-coins. You may not find your favorite coin to purchase on one platform, but find it on another. Different platforms also may require payment of those transaction/gas fees in different cryptocurrencies like Ethereum or Solana. This should be researched before signing onto different platforms where trial-and-error may cost you.
2. Crypto Staking and Lending. Staking is a way to “validate” crypto transactions in the blockchains with a “Proof of Stake (PoS)” protocol. When you stake, you essentially lock coins in a crypto-wallet, and a PoS network uses your coins to validate transactions. To reward stakers for loaning their coins to the network, the network rewards you in more coins. The concept is not dissimilar to earning “interest” at a bank for leaving your money in a savings account (which then the bank can use to invest or distribute loans where the bank will make more money on). The difference is, instead of earning 1-2% interest at the Bank, staking your crypto coins can earn you up to 20%! Note, like with every other strategy – some research is required if you wish to partake in staking. Some trading platforms have this functionality built-in, while others do not. Alternatively, there are staking-specific wallets and applications that can be downloaded and utilized.
3. Participate in “Mining” to earn coins by validating transactions through those blockchains that use a “Proof of Work (PoW)” protocol, which requires miners. If you have the adequate super-computer power to mine efficiently, winning miners are rewarded in crypto-tokens.
4. Launch your own Crypto-Asset: Create your own blockchain or cryptocurrency and launch it through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO). Similar to an Initial Public Offering (IPO), if you can convince enough investors to buy your ICO, millions and in some cases billions of dollars have been raised with just a whitepaper on your project and a website. Because ICOs are currently unregulated, there have been many fraudulent cases and scams where millions of dollars were run away with after an ICO that went dark. Another way to launch your own crypto asset, is to launch your own NFT and sell it. More on NFT’s later in this report.

%2Fuploads%2Fcrypto-universe%2Fcover1.jpg&w=3840&q=75)