Unlocking New Dimensions: Restaking’s Role in Advancing Crypto Security and Market Reach
17 July 2024•
The cryptocurrency sector witnessed the emergence of a new narrative in 2023: restaking.
This novel mechanism not only extends the economic security of a blockchain network but also catalyzes the birth of a new multi-billion dollar industry. While Ethereum is a key player, this narrative encompasses a range of protocols, suggesting a broad impact across the web3 ecosystem.
How Restaking Works
Restaking is a strategy within the blockchain ecosystem where tokens already staked on one network are additionally staked on a different blockchain network. This process not only introduces new terms for the loss of stakes (slashing conditions) but also provides the opportunity for additional rewards.
Comparable to ‘Merger Mining’ in Proof-of-Work networks, restaking enables users to utilize the same hardware to secure multiple blockchains, thus earning extra rewards. This strategic approach allows investors to compound their returns by deploying rewards from one platform in further staking opportunities on another.
In the decentralized finance (DeFi) landscape, restaking is a pioneering concept led by platforms like EigenLayer, which facilitate ETH stakers in securing multiple blockchains simultaneously. While Ethereum is a major player, other blockchain protocols such as Cosmos (via Persistence One) and Solana (with protocols like Jito and Marginfi) have also embraced similar restaking mechanisms.
Ethereum, given its consensus mechanism, is renowned to be one of the most secure crypto-economic systems on the blockchain—with over 31.7 million Ether (worth approximately US $100 billion) reinforcing the network—making it an ideal candidate for extended staking practices.
Why Restaking?
Restaking allows users to stake tokens on a network where they have already allocated tokens to another network. The primary motive is to maximize returns on investment (ROI) by earning additional rewards. In Ethereum’s context, restaking lets users stake their ETH on Ethereum and simultaneously on other protocols, effectively securing multiple networks at once and increasing their potential rewards.
Restaking also offers several nonfinancial benefits. Validators, for instance, can provide activated validation services, contributing to oracles, bridges, and improving data availability. This expanded role not only enhances the ecosystem’s functionality and reliability but also creates a more interconnected and robust network, rewarding validators with additional incentives for these enhanced services.
Staking vs. Restaking: Understanding the Processes
Traditional Staking:
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains operate on a consensus mechanism where token holders pledge their cryptocurrency to support network operations, earning staking rewards derived from transaction fees and token inflation. Typically, staking yields range from 3% to 10% annually on held assets. The staking process can vary in complexity from simple actions, like clicking a button on a centralized exchange, to running a full validator node.
- However, staked crypto generally contributes to validating blockchain transactions through a validator node. The complexity arises mainly for those running their nodes, while most users prefer delegating their crypto to experienced operators.
Restaking:
- Restaking builds on traditional staking’s foundation by allowing the use of staked tokens (often locked and illiquid in standard staking) for additional staking on different networks. This is enabled by innovations like Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs), which represent the staked assets and remain highly liquid. This allows users to engage in other DeFi protocols without needing to unstake their assets, creating multiple income streams.
- By utilizing these LSD tokens, and even initially locked ETH, EigenLayer introduced a system where staked ETH can be “restaked” for varied purposes, enhancing the utility and efficiency of the staked capital.
Glossary
Merger Mining
Merger Mining refers to combining the mining process of two different cryptocurrencies using the same algorithm. This allows miners to secure both networks and earn rewards from both, all while using the same computing power they would typically use to mine just one.
Validator node
Validator node checks and verifies the transactions and other data added to the blockchain to ensure everything is accurate and follows the network’s rules. By doing this, validator nodes help maintain the integrity and security of the blockchain.
Liquid Staking Derivatives
Liquid Staking Derivatives are a way for cryptocurrency holders to participate in network operations, like voting on changes, without locking up their assets. Instead, they receive a derivative token representing their staked assets, which they can trade or use while still earning staking rewards.
Economic and Security Impact
From an economic and security perspective, restaking allows multiple networks to be secured using the same equity stake, enhancing the overall security of the ecosystem while maintaining capital efficiency. The economic security in PoS networks like Ethereum deters attacks by making them financially unfeasible for attackers, considering the substantial capital at stake.
Restaking’s ability to leverage Ethereum’s substantial economic security helps reduce barriers for new networks, allowing them to access necessary security resources without substantial upfront capital. This is particularly advantageous for emerging projects looking to tap into venture capital or other forms of funding.
In conclusion, restaking not only increase the potential yield from staking activities by allowing participation in multiple protocols but also maintains liquidity and offers high flexibility in financial engagements. This dual advantage positions restaking as a significant evolution in the blockchain and DeFi sectors, promising ongoing growth and innovation.
How Staking and Restaking Work on Ethereum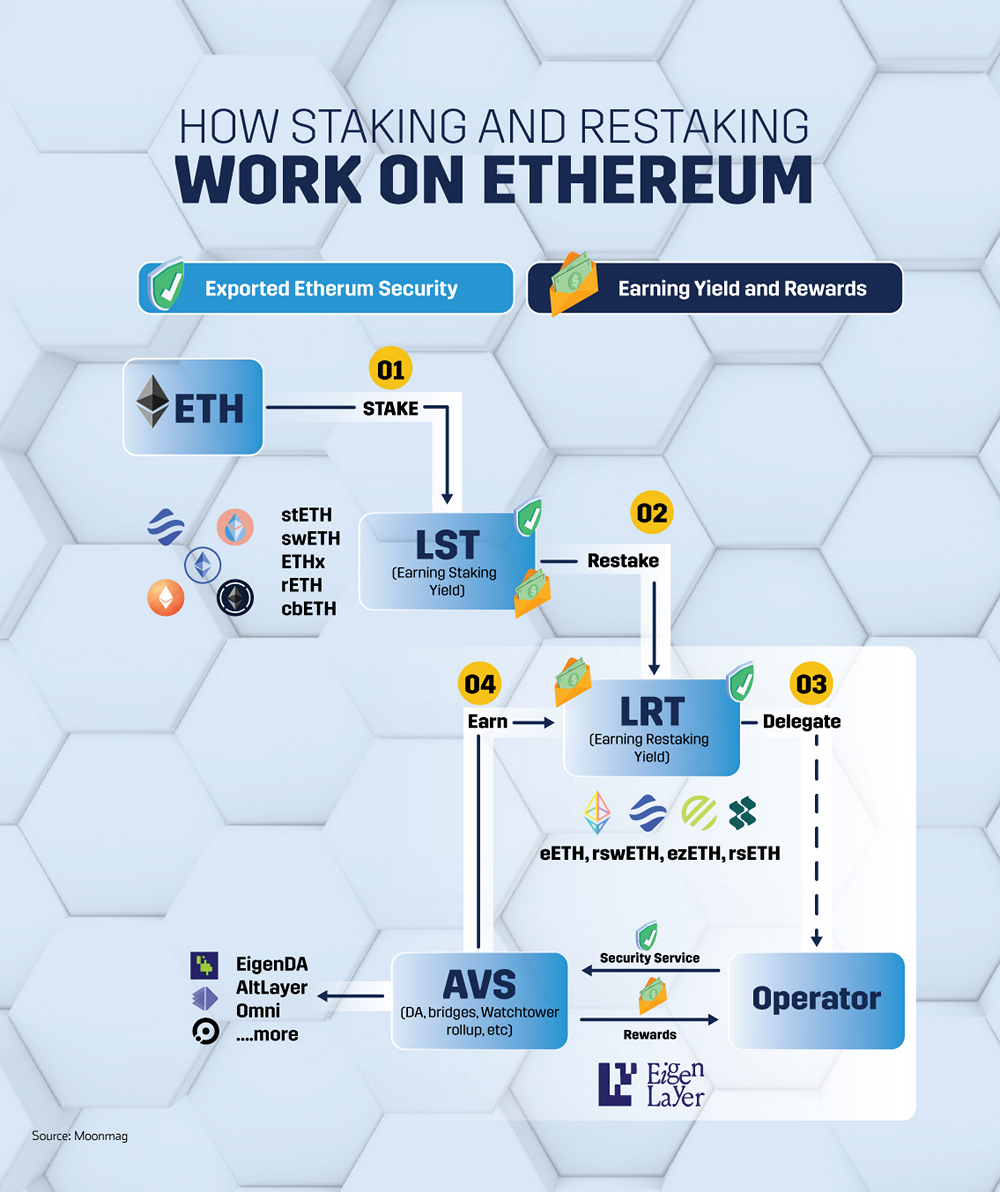
Impact of Restaking on the DeFi Ecosystem
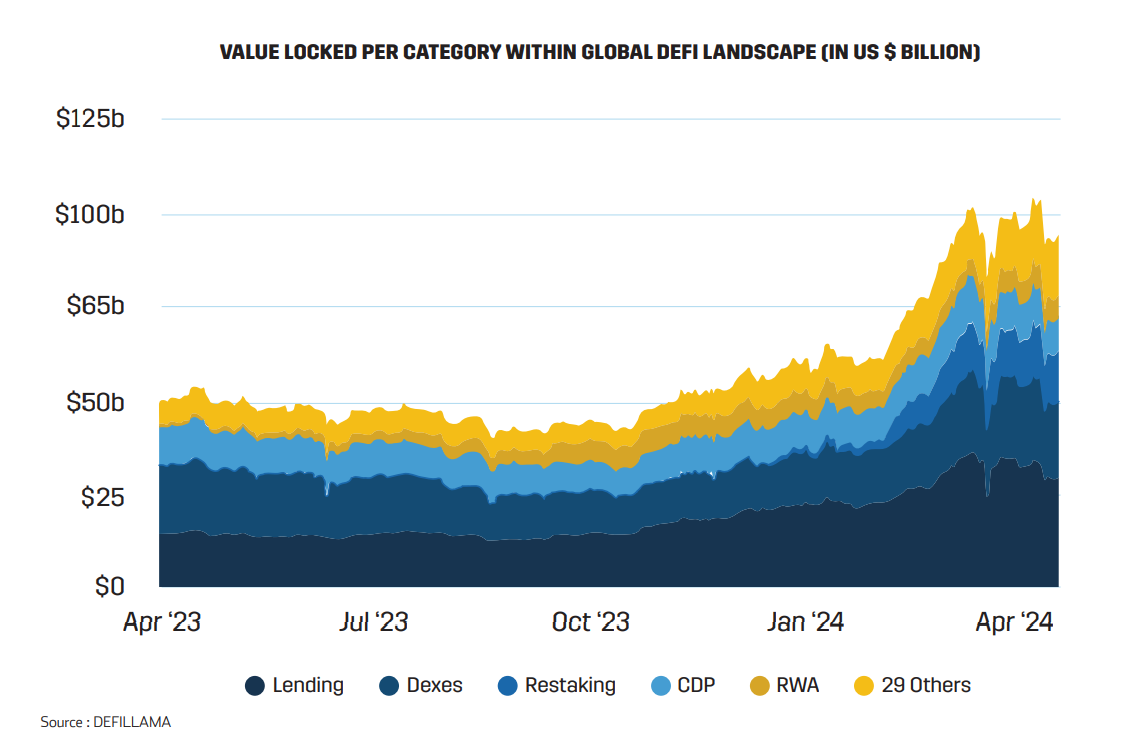
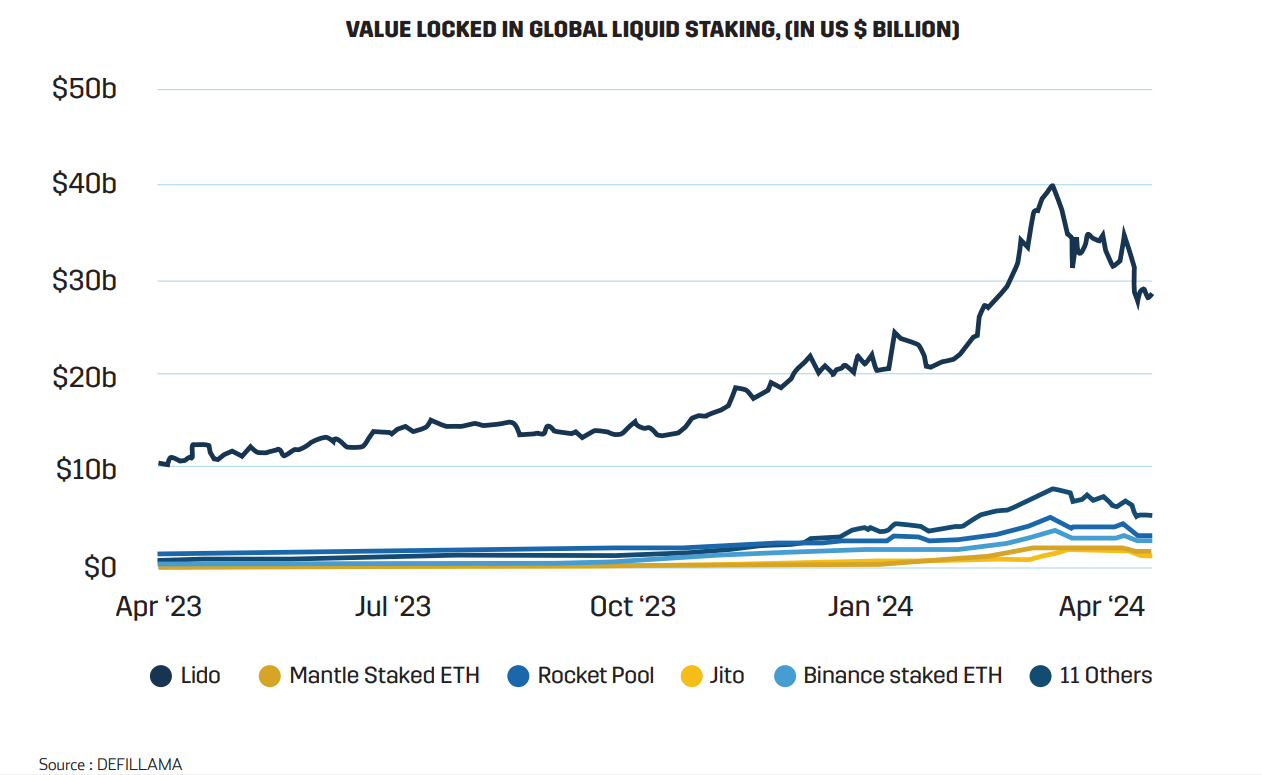
Since 2021, the DeFi landscape has experienced a transformative shift. Liquid staking has emerged as the dominant sector, now accounting for US $45 billion of the approximately US $100 billion DeFi industry as of April 2024. This significant change marks a departure from previous years, when DEXs (Decentralized Exchanges) and lending platforms were the primary drivers of DeFi activity.
Infobyte: Value Locked Per Category Within Global Defi Landscape (in US $ Billion)
Infobyte: Value Locked in Global Liquid Staking, (in US $ Billion)
At the heart of this revolution is now the EigenLayer, which is significantly enhancing the capability of Ethereum by enabling ETH to secure multiple blockchains simultaneously. The choice of Ethereum as the foundation for EigenLayer’s operations is strategic, given its inherent crypto-economic security with over 26.6% of its ETH supply staked.
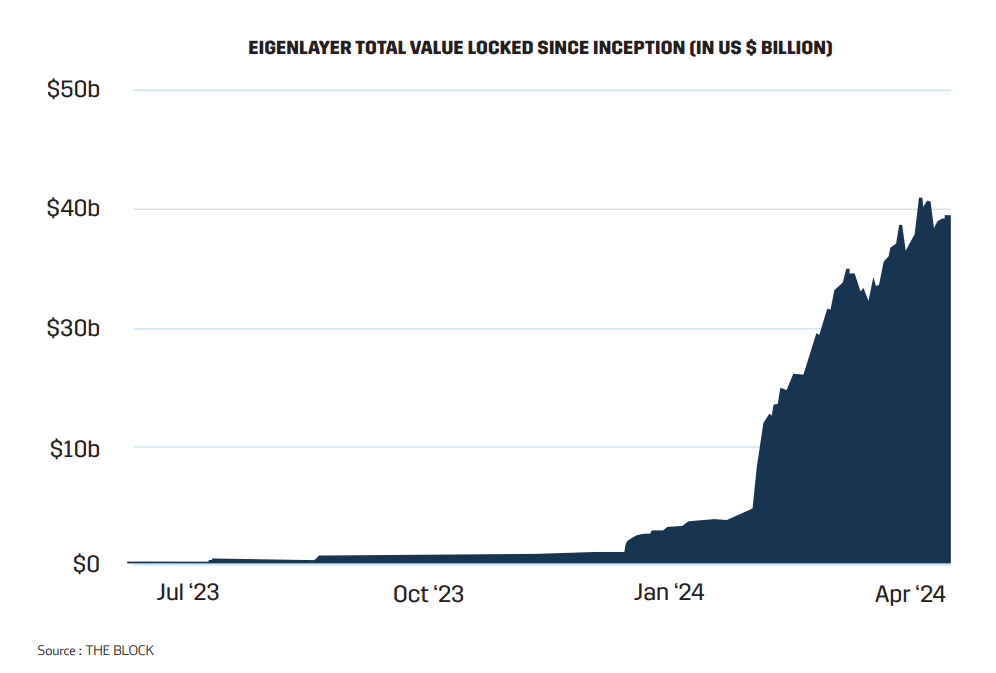
The impact of this innovation is clearly reflected in the growth of Total Value Locked (TVL) in restaking protocols, which soared from US $1.1 billion on January 1, 2024, to over US $13.97 billion by April 21, 2024. This growth trajectory establishes EigenLayer as a leading innovator in the staking domain, with its TVL nearing US $15.15 billion as of April 20, 2024—an eleven-fold increase since the beginning of the year.
Infobyte: EigenLayer Total Value Locked since Inception (in US $ Billion)
Looking ahead, EigenLayer plans to launch EigenDA, which will be the first Actively Validated Service (AVS) on the platform. AVS are services that undergo continuous real-time validation by the network’s validators, ensuring adherence to security protocols and operational integrity. This active validation contributes to a more secure, scalable, and efficient blockchain ecosystem. EigenDA is expected to leverage restaking to reduce transaction fees for rollups, potentially transforming the scalability of decentralized applications across various sectors, including gaming and social media, where high transaction costs have traditionally hindered broader adoption.
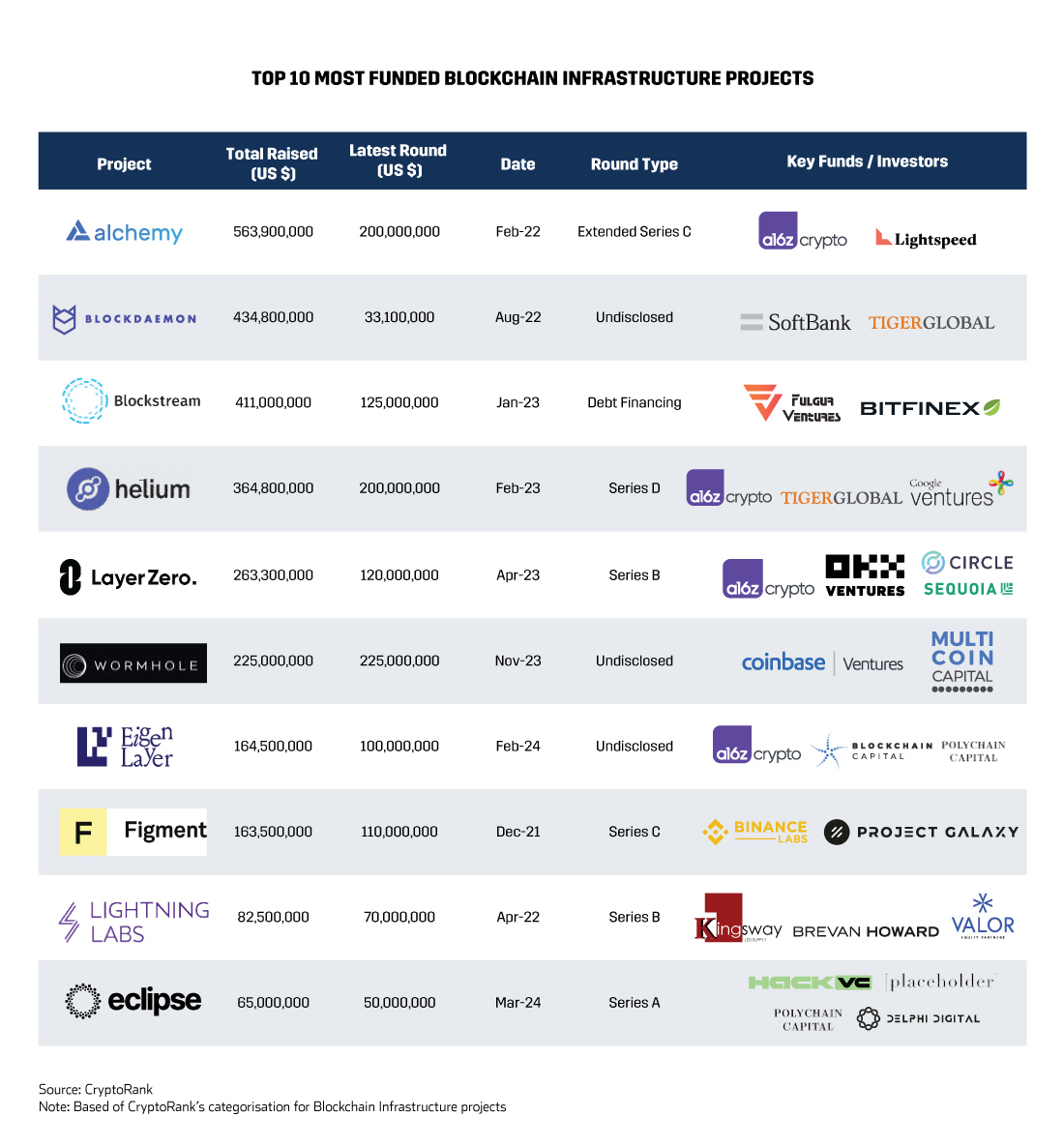
The potential of EigenLayer continues to attract significant investment, evidenced by a US $100 million funding round in February 2024, led by a16z. This investment underscores the confidence in EigenLayer’s potential to further revolutionize DeFi, making it a critical component of the future blockchain infrastructure. The project’s total funding has now reached $164.5 million, placing it among the top 10 most-funded blockchain infrastructure projects—excluding public funding sources like initial coin offerings (ICO).
Restaking is reshaping the cryptocurrency landscape by enhancing capital efficiency and network security. As this mechanism becomes more integrated into major blockchain operations, its impact is likely to expand, fostering more robust and economically secure networks. For those new to the cryptocurrency world, the evolution from simple staking to complex restaking strategies represents both an opportunity and a learning curve.
Top 10 Most Funded Blockchain Infrastructure Projects
To learn more about the innovations driving blockchain forward – read the full report here.

%2Fuploads%2Finnovations-blockchain%2Fcover22.jpg&w=3840&q=75)