The Impact of Egypt’s Currency Devaluation on Local Startups
21 March 2024•
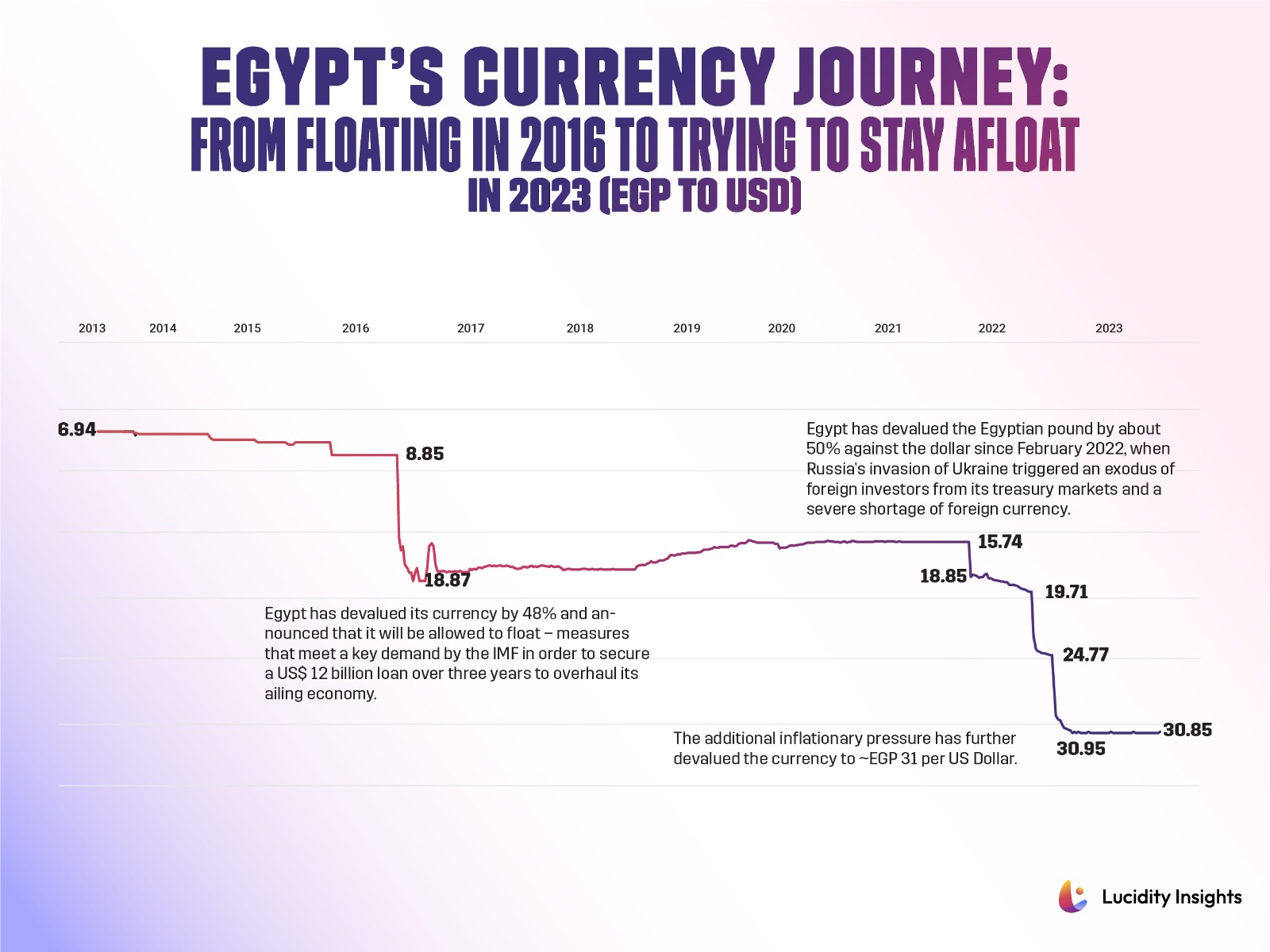
The Egyptian currency has witnessed major volatility in the past two years in particular, after enjoying a relatively stable currency position since the Egyptian Pound adopted a free-float approach in November 2016. The Egyptian Pound has changed its pegging to numerous standards, starting with the gold standard from 1885 to 1914, to the British pound from 1914 to 1962, and to the US dollar from 1962 to 1989, until it was eventually floated. While the currency was floated, it was tightly managed by the Central Bank of Egypt until 2001, subsequently which the country depended on utilizing policies to manage the float. Eventually the Central Bank was forced to end the managed-float regime to adopt a free float in November 2016, a move that caused the Egyptian Pound to fall twofold in value.
Infobyte: Egypt’s Currency Journey from 2016 to 2023 (EGP to USD)
While the 2016 devaluation was due to the free float, and seen as a natural correction, the abrupt devaluation in 2022 is due to systemic economic and financial challenges facing Egypt. This has left Egyptians to grapple with the rising prices of run-away inflation, coupled with a foreign currency crunch, which has led to an informal exchange rate of 50% over and above the official exchange rate. For example, at the end of 2022, the black-market rate to buy a US Dollar was EGP 54.85 while the official exchange rate is EGP 30.90 to the dollar. The Israel-Gaza war has also been a factor, taking a toll on the currency and contributing negatively to the inflationary environment, which is still high at over 35%.
Impact on the startup ecosystem
Once economic woes coupled with a devalued currency regime environment is present, it has an inevitable knock-on effect on a country’s startup ecosystem. There are three areas where this impact is seen most visible: (a) limiting access to funding, (b) limiting access to talent, and (c) challenges around maintaining revenues.
Access to Funding
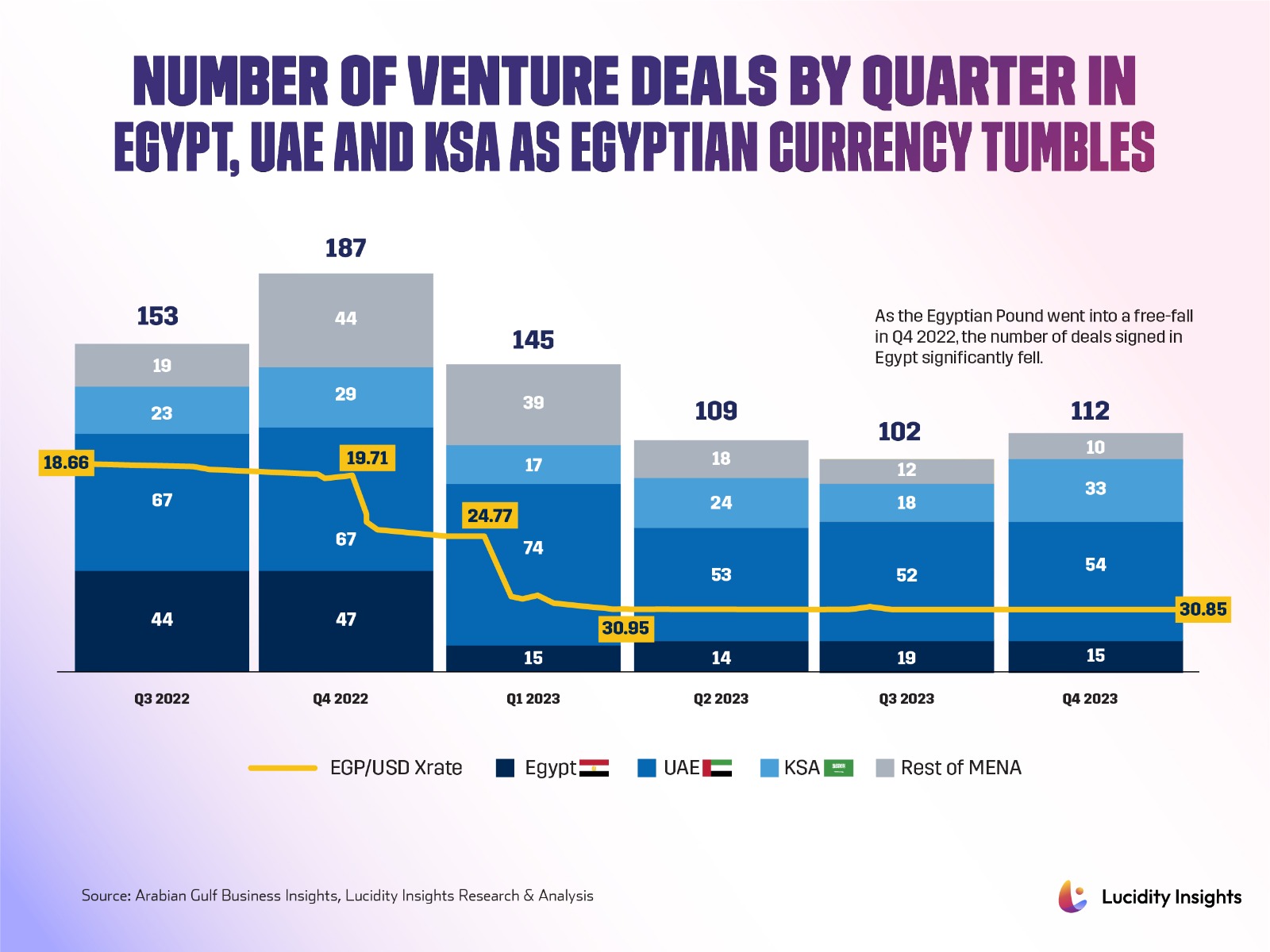
Access to funding is beginning to dwindle. The number of startup funding deals fell by 70% during the first half of 2023, in comparison to the first half of 2022. MNT-Halan’s debt deal made up the majority of Egypt’s deal flow during the first half of 2023 and removing that deal alone would imply a fall of 90% from US$ 324 million in H1 2022 to a meagre US$ 31.8 million in H1 2023.
There’s another element to the access to funding piece, particularly for those startups that have already closed rounds of funding. Firstly, the devaluation of the Egyptian Pound has meant that overnight the valuation of these startups have been halved. If the startup has international costs in supplies or manpower, purchasing power has been halved, while the revenues coming in is worth half of what they were worth in 2021. These startups have a hard sell, when speaking to investors as they look for follow-on funding – as the valuation of their startup has dropped significantly. Without an innovative and ambitious strategic plan on how to get out of this mess – these startups may spend the next few years just getting back to the valuations they had achieved a few years ago. This doesn’t smell like an opportunity VCs would be hungry for.
Infobyte: Number of Venture Deals by Quarter in Egypt, UAE and KSA as Egyptian Currency Tumbles
Lucidity Insights reporters spoke to Egypt’s most active investors, and they all told us that Egypt is definitely going through a crisis. But those investors who were around during the 2011 uprisings and economic downturns also said that it is not as doom and gloom as it may seem. Tarek Assaad, Founding Partner of Algebra Ventures said, “This is a very challenging time for Egypt. I’ve never seen this amount of turbulence in the economy. But particularly for tech startups, the picture is not as bleak as the rest of the economy, and there is still tremendous opportunity. Valuations may be halved today, but this will change. Long term, so long as the fundamentals are there, I am confident things will work out.”
Another element contributing to dwindling access to capital, is the fact that many VCs have raised their venture funds in US dollars. This means that they will have to be careful to hedge foreign-currency risk and will generally stay away from investing in risky countries like Egypt and Pakistan, and instead focus on investing their funds in startups based in countries that have currencies pegged to the US dollar. That’s just how the game is played.
Access to Talent
Egypt has high-quality university graduates and has long been regarded as a hotbed for sourcing developers for the Middle East’s tech ecosystems. But instead of these talents staying in Egypt to contribute to the country’s tech ecosystem, many have taken jobs abroad in the GCC and in Europe. Those that have stayed are working remotely and earning salaries in US dollars from international firms.
Bassem Raafat, Principle at A15, a venture capital firm in Cairo spoke on this. “Egyptian startups are having a hard time retaining top talent. GCC and global employers are making attractive offers to recruit Egyptian talent - sometimes requiring relocation, but often allowing for remote work out of Egypt. They are providing USD compensation, which means 5X current EGP salary levels in the current macroeconomic climate, making these offers very difficult for an Egyptian startup to compete with. The only sustainable solution we see is for Egyptian startups to start generate dollarized revenues, allowing them to become more competitive, while also continuing to offer an attractive place to work in terms of culture, personal development and career progression.”

Revenue Management
As we learned earlier, revenues streaming into these startups are in Egyptian pounds, which are unstable – and are worth half of what these same revenues were worth in 2021. Thus, investors’ appetites are also impacted negatively resulting in a “a drop in the inflows from regional VCs” according to Mr. Mohamad El Ghannam, Principal at Flat6Labs, a leading accelerator based out of Egypt.
On the other hand, after the Egyptian Pound’s devaluation, Egypt has become one of the least expensive places for development. On the flipside, the challenge is that startups have to grow at a pace much faster than the economy just to mitigate devaluation challenges. Therefore, it won’t come as a surprise that many startups are expanding into both Saudi Arabia and the UAE for market expansion. If the currency further devalues, any incoming cash in the future will further weaken a startup’s position.
On top of the host of challenges facing Egypt today, another challenge has been created; and that is, in effect, brain drain. As Egyptian startups look to shift their base to more stable countries with greater access to capital and stable revenues, top entrepreneurial talent is saying “goodbye” to Cairo, and saying “hello” to cities in Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
Relocation of HQ to another country is a function of getting greater exposure to stronger investment options, as startups pursue funding and being closer to a larger target customer base – with greater spending power. Egyptian startups recognize that the purchasing power is quite high in both the UAE and Saudi Arabia, so being near these customer bases is a natural choice. The incentives provided are also a lot more attractive, which often include partial subsidy of employee salaries (depending on startup size), free-of-charge consultation from government players (such as the case with Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Investment), rent free offices, tax relief and a one-stop-shop for all governmental papers and licenses to streamline the registration process.
For Egypt to succeed and become a tech hub of the Middle East and Africa region, the solution is clearly to gather more financing options for startups. VCs like Modus Capital partnered with USAID to launch a venture builder in Egypt. 500 Global has also been investing in the ecosystem, and opened an office in the country in December 2022, with an intent to support 200 startups. Leveraging the lower cost of talent as well as startups at more attractive valuations are promising, however challenges of remittances and repatriations deter investors in such an unpredictable environment.
Egypt, however, has proven itself to be attractive and, most importantly, resilient, over the years. Once the dust settles, with Egypt becoming more geopolitically relevant, the startup ecosystem will surely garner more interest; and this is something the ecosystem undoubtedly needs, but also deserves.


Next Read: Meet Egypt's Pioneering Accelerator & Incubator Ecosystem (Ebni, SBC, AUC, F6L)

%2Fuploads%2Fegypt-2024%2Fcover20.jpg&w=3840&q=75)