Delivered to Your Doorstep: The Journey of Food Delivery and Its Impact on Modern Lifestyles
04 June 2024•
From the ancient streets of Rome to the digital doorsteps of the 21st century, explore the intertwining of food delivery with technological innovation, societal shifts, and changing consumer preferences. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of food delivery, where convenience, technology, and tradition blend seamlessly to feed the world.
Navigating the Intersection of Food Delivery and FoodTech
In today’s fast-paced world, where time is precious and convenience is key, the concept of food delivery has become an integral part of our daily lives. But what does this term truly entail, and how is it intertwined with FoodTech? Essentially, food delivery is the service of transporting various food items, ranging from ready-to-eat meals to groceries, from their origin – such as restaurants, supermarkets, or local cooperatives – straight to consumers’ doorsteps. This service, which began as a straightforward solution to dining at home, has now evolved into a complex and diverse market, addressing a wide array of consumer demands and preferences.
Many people may think that FoodTech boils down to the app people use for ordering food online. However, it is far more expansive than that. The adoption of technology in the food industry has many potential ramifications and impacts from supply chain innovations to food processing technologies and the embedding of sustainability practices. It leverages advanced technologies such as AI to tailor meal suggestions to individual tastes or employs drones as new and innovative delivery methods. The global food delivery market was estimated to reach over US $1 trillion dollars in 2023 and is expected to reach US $1.79 trillion by 2028 attesting to how deeply ingrained food delivery has become in our daily lives. Throughout its history, the food delivery industry has continually evolved, driven by societal shifts, shifting consumer preferences, and rapid technological advancements; and these are trends that persist into the present day.
The History of Food Delivery
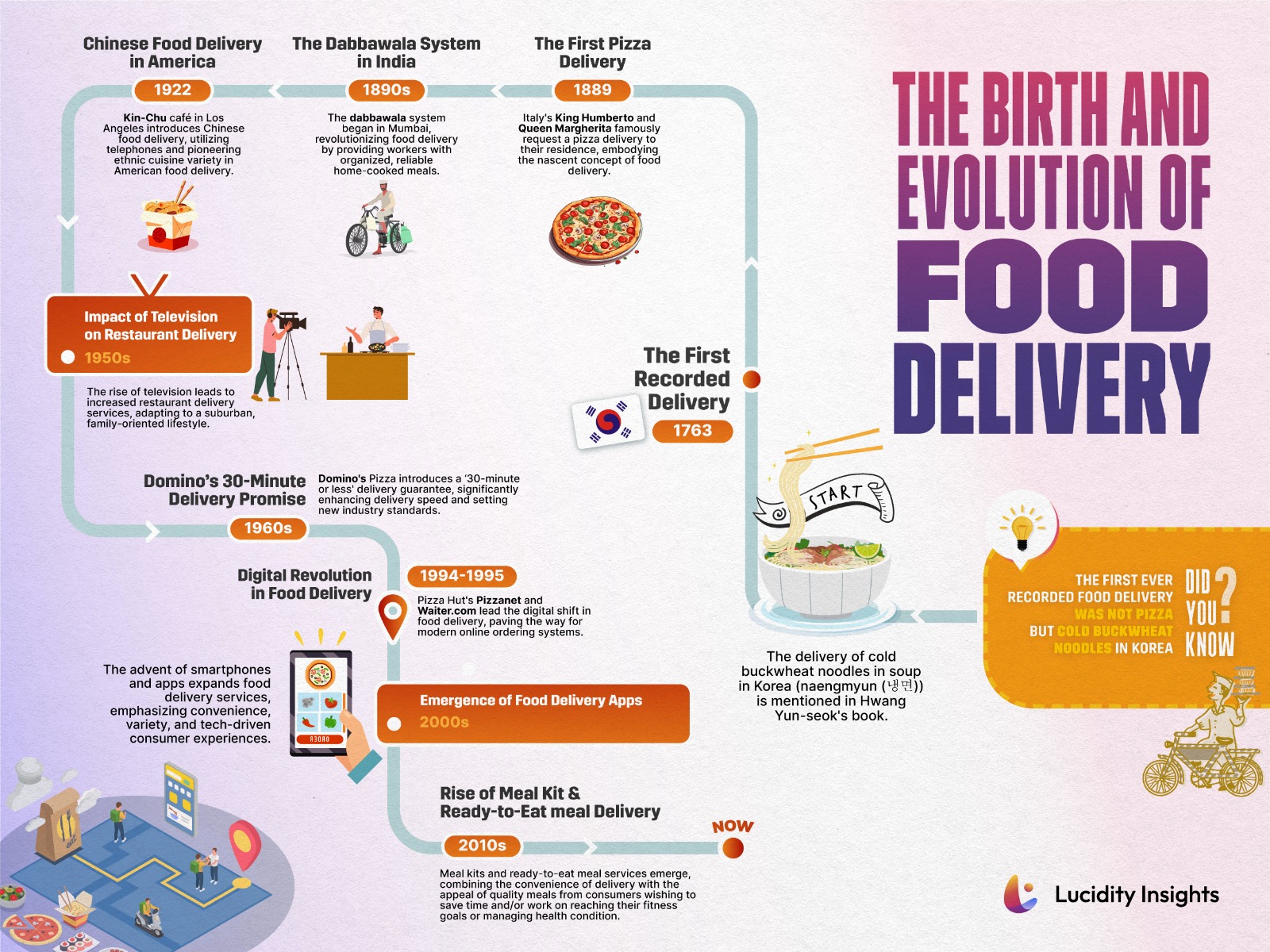
The birth of the restaurant culture traces back to the streets of ancient Rome, around 753 B.C. to 476 A.D., where Thermopolium, the Roman equivalent to modern-day fast-food joints, served ready-to-eat meals. These establishments catered to the Romans’ desire for quick and convenient meals, much like our fast-food culture today. In the 11th and 12th centuries, similar establishments began appearing throughout Asia. By the 16th century, the emergence of Tea Houses laid the groundwork for the contemporary restaurant culture.
 Infobyte: The Birth and Evolution of Food Delivery
Infobyte: The Birth and Evolution of Food Delivery
Pinpointing the precise genesis of food delivery eludes historians, yet evidence from the 18th and 19th centuries provides some clarity. Among the earliest recorded instances is the delivery of cold buckwheat noodles in soup in Korea, an event Hwang YunSeok vividly recounts in his narrative, marking a special occasion in July 1768. Similarly, a celebrated moment in 1889 saw Italy’s King Humberto and Queen Margherita, during their sojourn in Naples, famously request a pizza delivery to their residence, embodying the nascent concept of food delivery.
The advent of the first formal meal delivery service unfolded in 1890, against the backdrop of British India’s rapid urbanization, which ushered numerous workers into the rapidly growing metropolis of Mumbai. Grappling with stringent work schedules and constrained lunch periods, the burgeoning workforce’s appetite for convenient dining solutions surged. Seizing this opportunity, Mahadeo Havaji Bachche launched a pioneering service with an initial cadre of approximately one hundred men. These “Dabbawalas” — literally, “one who carries a box” — emerged as the lifeline for Mumbai’s labor force, adeptly fulfilling the city’s escalating demand for accessible and efficient meal delivery options.
By the 1920s, take-out had become a staple in American culture. In 1922, capitalizing on this trend, the Kin-Chu Café in Los Angeles started advertising themselves as the “only place on the West Coast making and delivering real Chinese dishes,” underscoring the growing popularity of food delivery services in the United States. During the Second World War, London faced constant bomb threats. To ensure the well-being of citizens, meals were delivered across the city, a practice that continued post-war in countries like the United States and Australia, often to aid veterans.
The cultural landscape of the 1950s, profoundly influenced by the advent of television, saw families spending more time at home. This shift led to a decline in restaurant patronage, prompting many to introduce delivery services. Pizza delivery, in particular, gained popularity in the United States, fueled by soldiers’ newfound taste for Italian cuisine. In 1954, the Meals on Wheels program commenced in Great Britain, initially aiding the disadvantaged and home-bound. This concept of delivering hot meals soon became a global phenomenon, extending a lifeline to millions of seniors worldwide.
In the 1990s, Pizza Hut introduced PizzaNet, marking one of the earliest forays into the online world. Although its service was initially limited to residents of Santa Cruz, PizzaNet played a crucial role in sparking the development of online delivery services. Following this pioneering effort, Waiter.com launched in 1995, initially serving the San Francisco Bay Area and collaborating with over 60 local restaurants to offer meal delivery.
As internet usage soared, New York entrepreneurs launched Seamlessweb in 1999, quickly followed by its main competitor, Grubhub. The two companies merged in 2011 (acquired by Just Eat Takeaway for US $7.3 billion on June 10, 2020), amidst growing competition from new entrants like DoorDash and Uber Eats. These platforms revolutionized the way customers interacted with local restaurants and broadened the reach of many eateries.
The first meal kit, Middagsfrid (“Dinner Peace” in English), was launched in 2007 in Stockholm, Sweden, by Kicki Theander (acquired for an undisclosed amount on May 31, 2017). This service was designed to assist families in enjoying home-cooked meals without the hassle of meal planning and grocery shopping. This innovative service, delivering bags of groceries right to customers’ doors, quickly became a success. The Middagsfrid brand quickly expanded across Germany, Denmark, Switzerland, and Belgium, sparking the emergence of numerous competing companies. This concept then migrated to the United States, where it resonated particularly with millennial urbanites. These young city dwellers, often valuing convenience and living in areas with limited access to grocery stores, found meal kits appealing. More recently, companies have started offering fully prepared, healthy meals addressing the growing demand for adequate, quality meals from consumers working on reaching their fitness goals or managing health conditions, further shaping the landscape of food delivery services.
The journey of food delivery, from the the first pizza delivery in the 1800s to the digital doorsteps of today, encapsulates a remarkable evolution, driven by the changing dynamics of society and the relentless march of technology. As we stand on the cusp of 2030, it’s clear that food delivery has transcended its initial purpose of convenience to become a multifaceted service that caters to a diverse array of consumer needs and preferences. With the food delivery market projected to grow exponentially, it is poised to further transform our eating habits, making it an indispensable part of our lives. As we look forward, the potential for growth and innovation in this sector is boundless, promising a future where food delivery remains at the heart of culinary convenience, quality, and sustainability. This ongoing evolution ensures that food delivery will continue to adapt, thrive, and revolutionize the way we consume food in a world that increasingly values efficiency, sustainability, and personalization.
The 7 Benefits Heralded by Food Delivery Apps
|
1 |
Customer Convenience & Time Savings |
Streamlining and outsourcing the entire food preparation process, from meal planning and grocery shopping to cooking and dish cleaning, significantly reduces time and effort for consumers. |
|
2 |
Increased Optionality |
The scope of delivery services has broadened to encompass a wider range of restaurants and supermarkets, as well as specialty stores like butcher shops and cake shops, offering consumers more choices and accessibility |
|
3 |
Increased Customer Base and Reach |
Collaborations with delivery services have allowed the F&B industry to access a wider consumer market, often leading to a notable increase in sales. |
|
4 |
Immediate Customer Feedback |
Leveraging technology for real-time customer feedback allows restaurants to quickly adapt their menus and oerings to match consumer preferences. |
|
5 |
Carbon Emission Reductions |
In theory, services like grocery delivery and meal subscription services, which use full trucks for multiple deliveries, achieve greater eiciency and reduce carbon emissions as opposed to multiples of consumers' single trips |
|
6 |
Promoting Healthier Lifestyles |
Food delivery services are promoting healthier lifestyles by providing easy access to healthy meals tailored to fitness goals and health management. |
|
7 |
Economic Impacts and Employment Opportunities |
Food delivery actively participates in driving the gig economy providing workers ways to save up extra money or cover fluctuations in income. |
Next Read: The Future of Food Delivery in Saudi Arabia: A Transformative Market on the Rise
Read more in the Special Report, ‘The Future of Food Delivery in Saudi Arabia’.

%2Fuploads%2Fsaudi-food-delivery%2Fcover21.jpg&w=3840&q=75)