Food Security and Trade: The Role Trade Plays in Nourishing the World
06 November 2023•
In the ever-evolving landscape of global food security, trade plays a crucial role in addressing the mounting pressures we face today.
The challenges are multifaceted, stemming from factors such as population growth, climate change, environmental constraints, and the dynamics of trade and markets. These challenges not only impact food production and availability but also have significant effects on food prices.
Trade is inextricably linked to ensuring food security, a topic that has become increasingly critical in the 21st century.
As the world's population continues to grow, the demand for food escalates, placing significant strain on global food systems. Projections indicate that by 2050, the global population will reach 9.7 billion, adding approximately 55-60 million people per year for the next three decades.
This exponential growth necessitates a corresponding increase in food production to meet the escalating demand. To put it into perspective, this annual increase is equivalent to adding the entire population of Italy to the world, for the next thirty years.
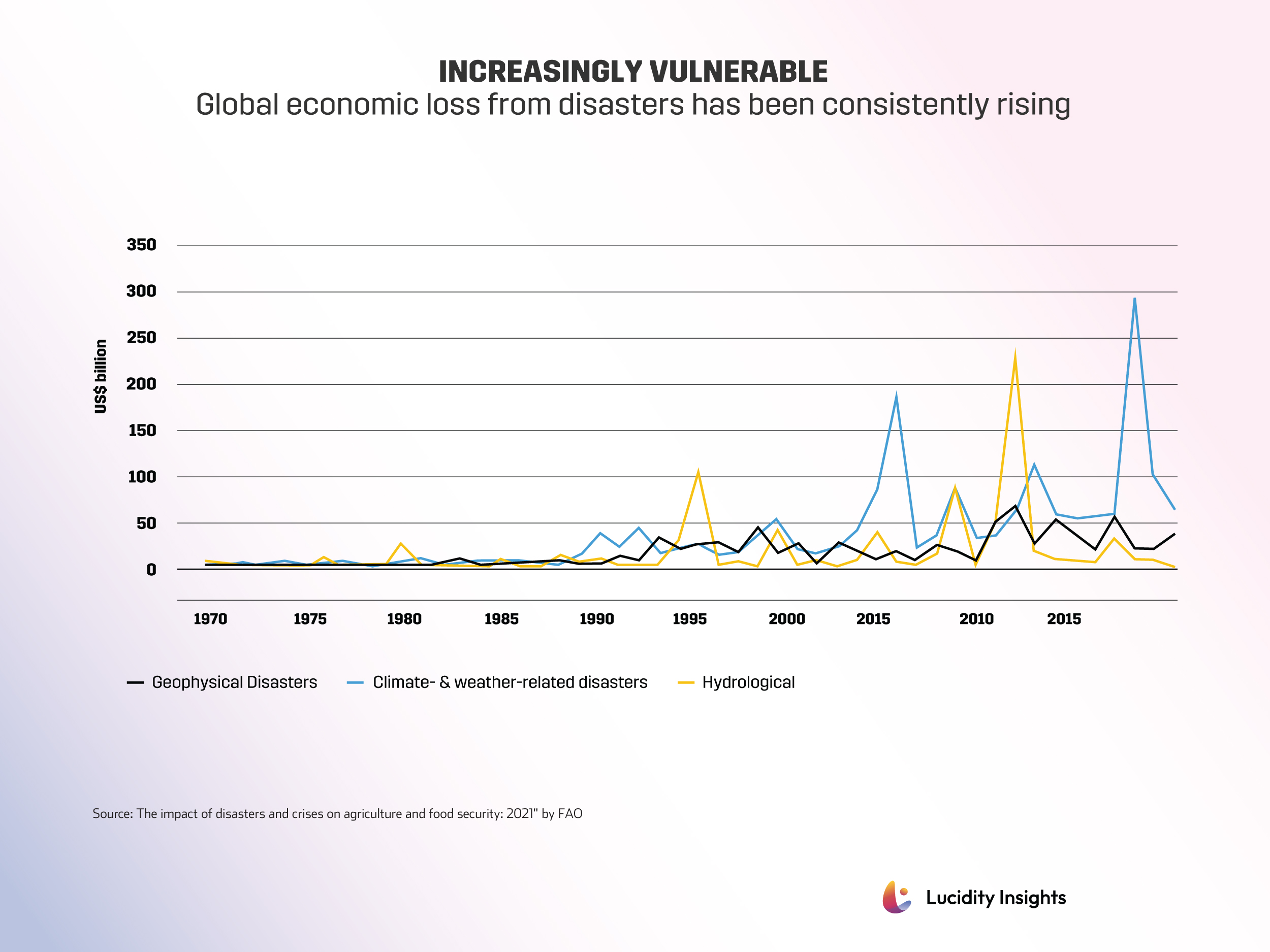
Climate change exacerbates the challenges faced by food production and agricultural productivity. We are already witnessing extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves, which severely impact crop yields and pose threats to livestock.
These disruptions further complicate farming practices, demanding that the agriculture sector adapts to mitigate the effects of climate change. Moreover, the loss of biodiversity also undermines food security, making food systems more susceptible to pests, diseases, and environmental changes, ultimately reducing agricultural productivity and food availability.
Another obstacle to increasing food production lies in the availability of arable land, freshwater sources, and energy.
Urbanization and industrialization have led to the conversion of agricultural land for non-agricultural purposes, resulting in a scarcity of fertile land. Efficient management of these resources is paramount to meeting the demands of a growing population.
Trade, on the other hand, plays a crucial role in supporting food security in multiple ways, falling under three broad categories:
1. Access to Food and Market Stability:
-
Trade ensures access to a diverse range of food products, stabilizing market fluctuations.
-
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization, more than 20% of the food produced for human consumption is traded.
2. Addressing Seasonal Variations and Geographic Disparities:
-
Trade helps overcome seasonal variations and geographic disparities in food production, ensuring a steady supply throughout the year. Countries in the Southern and Northern hemispheres can rely on each other due to their different growing and harvesting seasons.
-
Trade enables countries to overcome domestic production shortfalls caused by factors such as droughts, pests, or natural disasters, allowing them to import necessary food items from countries that can produce optimally.
-
Developing countries have significantly increased their imports of agricultural products, indicating improved access to food through trade.
3. Income Generation and Economic Development:
-
Trade opens up economic opportunities, generating income that contributes to poverty reduction. Smallscale farmers, for instance, can access new markets and receive better prices for their products.
-
Sustainable agricultural practices play a vital role in long-term food security.
-
Agricultural exports from developing countries have witnessed substantial growth, from $35 billion in 1990 to $335 billion in 2016, supporting rural livelihoods and economic growth in vulnerable communities, as estimated by the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI).
Promoting sustainable agricultural practices that enhance productivity, conserve resources, and reduce environmental impacts is essential. It is equally important for stakeholders, including governments and international organizations, to develop coordinated strategies, share best practices, and mobilize resources to ensure food security amidst the challenges posed by climate change.
Several nations have already initiated initiatives to bolster food security, with the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Japan, and Singapore among them.
In conclusion, trade is a key pillar in supporting enhanced food security. Establishing fair and transparent trade policies that enable access to diverse food sources, stabilize market dynamics, and ensure the availability of food is of paramount importance.
Building a resilient food production system that not only provides sufficient food but also emphasizes nutrition and affordability is crucial for the well-being and future of our growing population.
By addressing food insecurity, we can pave the way for a brighter and more sustainable future.




%2Fuploads%2Fsustainable-intl-trade%2Fcover.jpg&w=3840&q=75)