Types of Blockchain technology and their real world use cases
03 June 2022•
Not all blockchains are developed for trading cryptocurrencies, though that is the application that you likely hear of most often.

Blockchains can be deployed by private companies and even governments that understand the technology to utilize in real-world applications. Here are just a few examples of how blockchain technology can be deployed and employed:
a. Supply Chain Logistics and Monitoring (tracking products)
b. Secure and Efficient Voting Mechanism
c. Secure Storing and Sharing of Medical Data
d. Personal Identity Security
e. Real-time Internet-of-Things (IoT) operating systems
f. Music Royalties Tracking
g. Cross-Border Payments (without long wait times or intermediary bank charges)
h. NFT marketplaces (exchange)
i. Cryptocurrency Exchange
Now lets get into the different types of blockchains and some of their real-world examples of use-cases. There are 4 Types of Blockchain Technology:
1. Public Blockchain
2. Private Blockchain
3. Federated Blockchain / Consortium Blockchain
4. Hybrid Blockchain
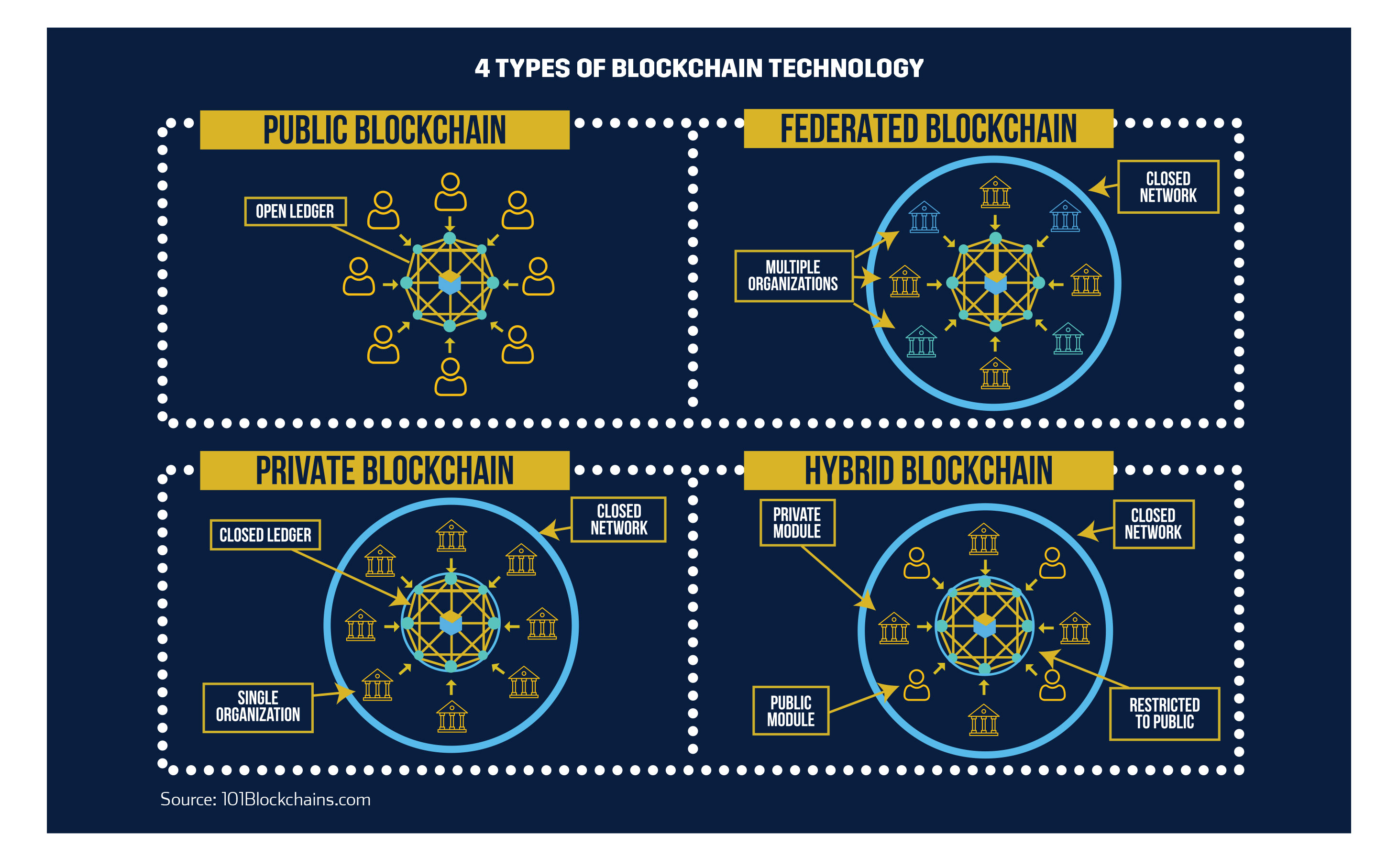
Public Blockchains are what we think about when we think about the original cryptocurrency blockchains, or “mother blockchain”; they are unrestrictive and open-sourced, which means anyone with internet connectivity can get access to the network and start validating blocks and sending transactions. This means that every node has access to read and write on the ledger, and anyone can download and add nodes to the network. To date, most all public blockchains use either the Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithms to validate transactions and the blockchain. It offers anonymity, which means no one can trace your transactions back to you. It’s fully decentralized, but it’s also slower compared to private blockchains. Public blockchains are truly “public” and democratic: ‘of the people, for the people, by the people’. The most famous and utilized public blockchains are Bitcoin’s (BTC) blockchain, Ethereum’s (ETH) blockchain, and Litecoin’s (LTC) blockchain.

Real World Applications for Public Blockchain Technology
Real-world applications and use-cases for public blockchain technology include Voting and Fundraising. Companies can fundraise using public blockchain technology or governments can conduct voting utilizing public blockchain technology in order to foster greater transparency and trust amongst donors and constituents. Countries like Estonia and Canada have already implemented blockchain technology as an efficient means of a voting mechanism in their country’s elections. In 2012 Estonia became the first government to implement blockchain governance by employing online voting using blockchain technology. The blockchain governance system ensured protection against future cyberattacks, provided stronger data security and data privacy, and dramatically enhanced auditability, while taking the whole voting process online. This also dramatically reduces the cost and operational inefficiencies of in-person voting or even mail-in ballots, such as poll worker shortages, complications of using paper ballots, prolonged wait-times, and numerous points of vulnerability with regards to corruption. There are many other countries working on blockchain governance today including Australia, Denmark, Switzerland, South Korea, Japan, Russia, and Sierra Leone.
Fundraising is another application that could utilize blockchain governance in the same way as blockchain voting.
Private Blockchains were developed because not all organizations or individuals could use public blockchains. This may be because businesses have competition sensitive and critical data that they cannot make public, should they wish to keep a competitive advantage and remain in business. Private blockchains were thus created that offers a completely private environment where only invited participants are eligible to contribute. Private blockchains are governed by a single authority, operates on a closed network and has a closed ledger, making it decentralized, which goes against the core philosophy of distributed ledger technology and blockchains in general; thus it is thought that private blockchains have a more difficult time building and achieving trust, as the centralized nodes make the last call. In addition, due to having fewer nodes, many have argued that private blockchains may be less secure than public blockchains. That said, private blockchains have much more streamlined and simpler data handling processes, which means faster output, better energy efficiency, and greater privacy versus public blockchains; private blockchains are thus much more scalable than public blockchains. Among the most famous and utilized private blockchains are Ripple’s (XRP) blockchain and Hyperledger’s blockchain.


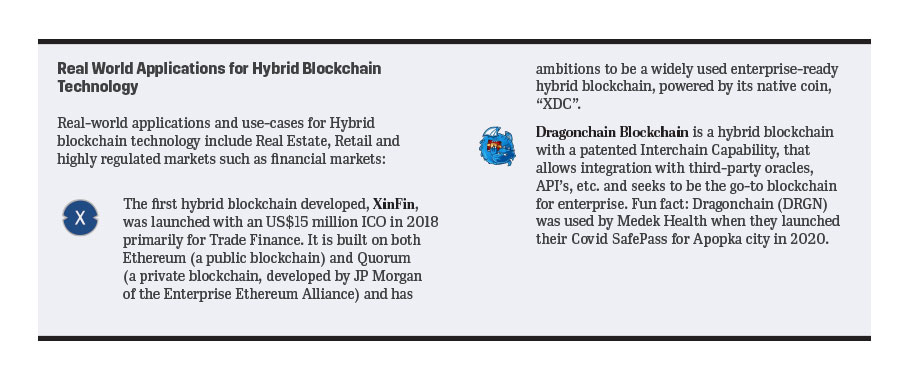
Hybrid Blockchains are blockchains that are controlled by a single organization, with a certain level of oversight provided by a public blockchain that is required to perform certain transaction validations. Hybrid blockchains are in essence a combination of the public and private blockchains; they provide the privacy benefits of a permissioned and private blockchain, while also providing the security and transparency benefits of a public blockchain. Hybrid blockchains generally work in a closed ecosystem without the need to make everything public, with rules that are changeable according to the needs of the network. Hybrid blockchains offers privacy while still connected to the public network and offers decent scalability compared to public blockchains. A disadvantage of the hybrid blockchain is that there is little to no incentive for participating and contributing to the network.

%2Fuploads%2Fcrypto-universe%2Fcover1.jpg&w=3840&q=75)