Opportunities for Innovation in the Region’s Proptech Space
28 March 2025•
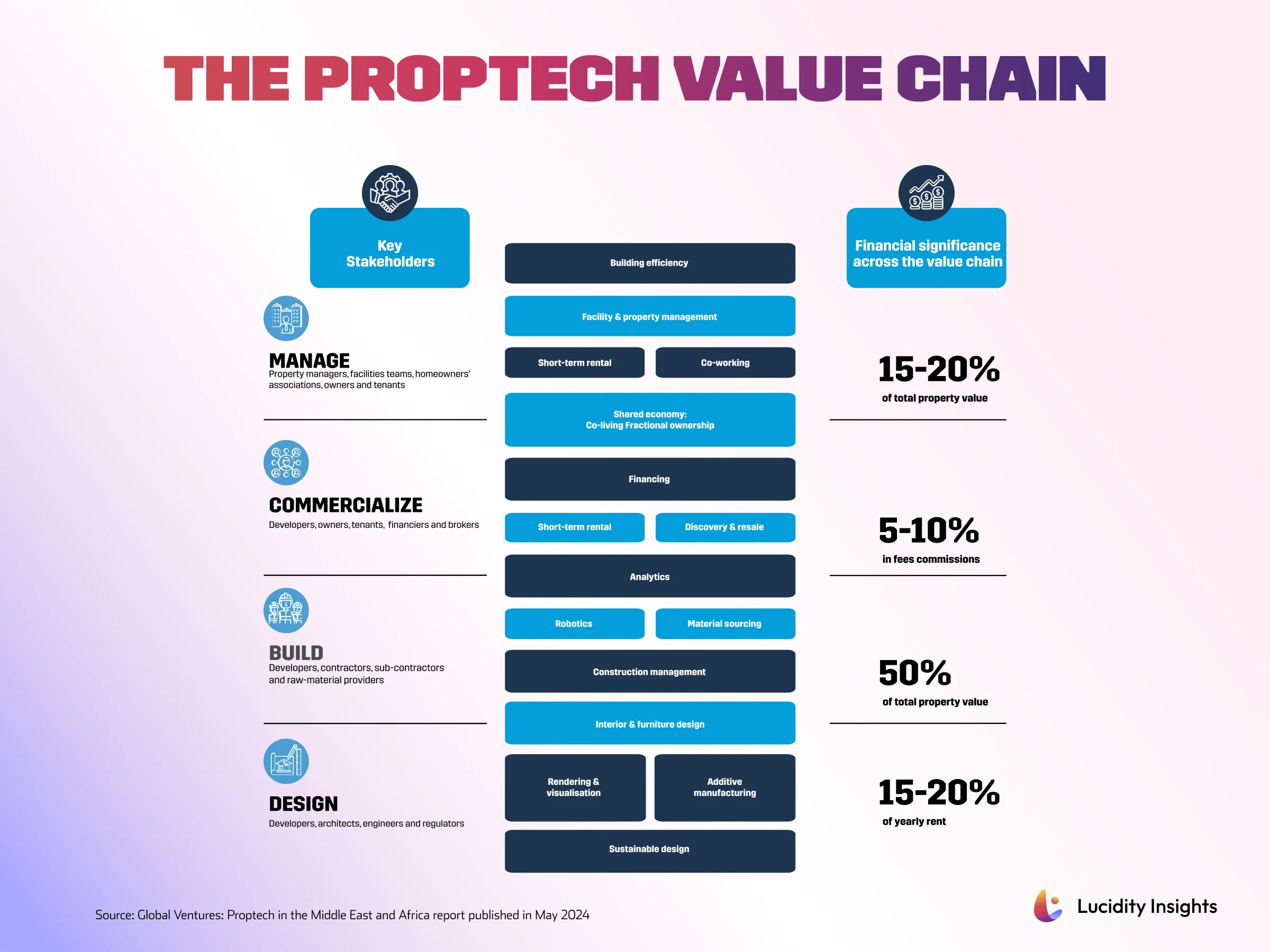
The Proptech value chain outlines key stakeholders and processes, ranging from property management to building efficiency, demonstrating how these elements contribute to the sector’s overall financial performance. Different processes and stakeholders are interconnected at various levels within the real estate ecosystem, highlighting the significant financial impact of activities such as efficient property management, innovative commercialization strategies, and thoughtful design.
The PropTech Value Chain
Let’s explore some examples of solutions and opportunities for innovation in Proptech across the 4 dimensions:
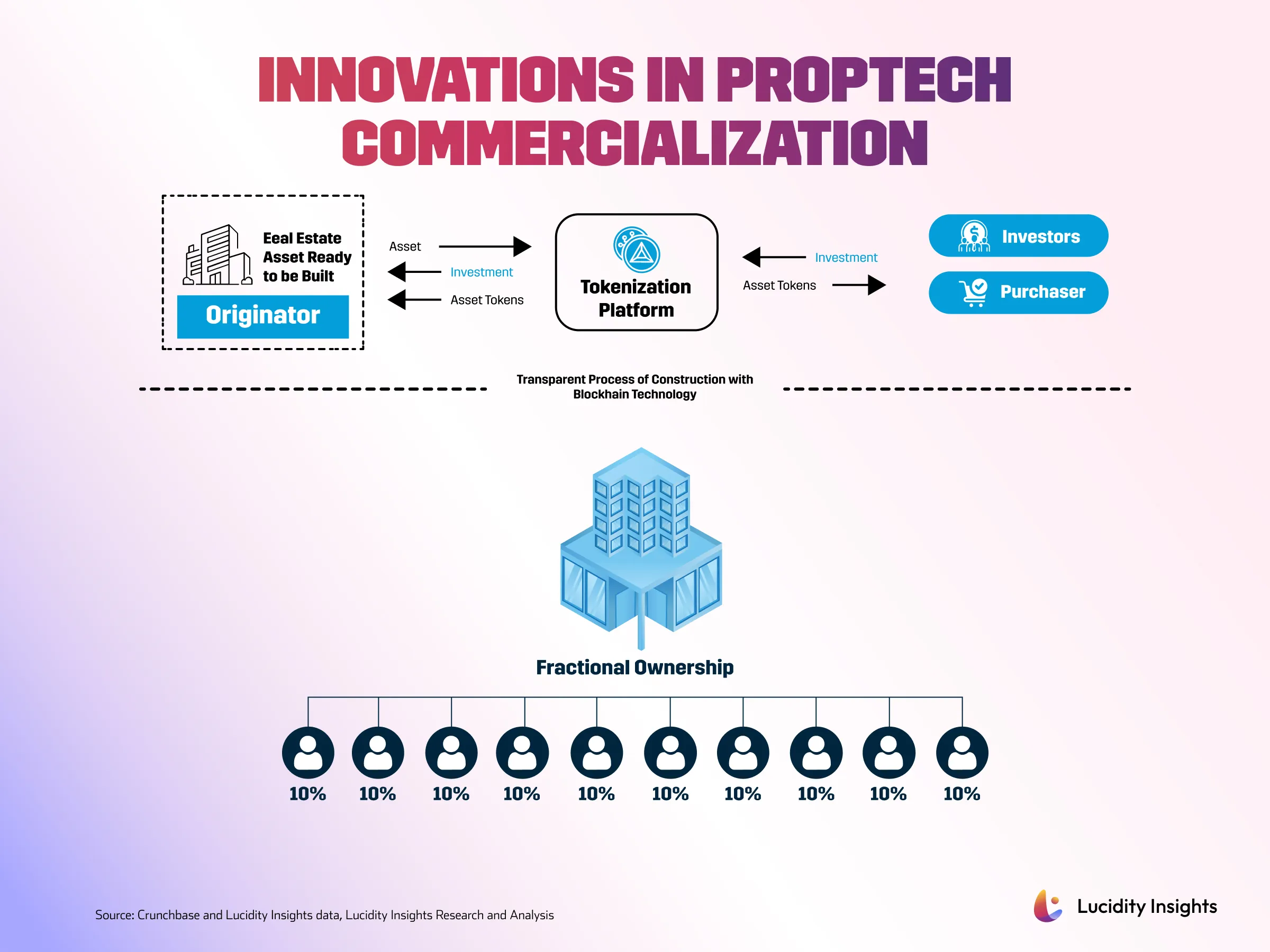
1. Commercialize
Driven by digitization, evolving consumer expectations, and economic pressures, alternative financing models are transforming property commercialization. Between 2019 and 2023, global VC funding directed at startups developing commercialization solutions reached US $5.5 billion. As millennials and Gen Z become more prominent market participants, there is an increasing demand for flexible and innovative financing models. Younger buyers, accustomed to digital transactions, seek investment opportunities that align with their mobile, less capital-intensive lifestyles. Solutions like fractional ownership and property tokenization are reshaping the market by offering greater inclusivity, flexibility, and simplified transactions.
2. Manage

Property management, which focuses on maintaining and optimizing real estate assets post-acquisition, often relies on outdated systems that fail to meet the evolving needs of consumers. As remote working becomes more common, there is a growing expectation for properties to support hybrid lifestyles, incorporating community-based living and coworking spaces. Consequently, property management strategies are shifting beyond mere space provision to enhance the overall user experience in an increasingly competitive market. Proptech solutions are filling the gaps left by legacy systems, improving areas such as energy management, security, and tenant experience, while offering more personalized and efficient property services.
3. Design

Advancements in technology are reshaping how spaces are designed, influencing their functionality, sustainability, and integration with the environment. To address cost constraints, lengthy approval processes, and the need for sustainable design, the industry is adopting innovative solutions to enhance efficiency and open up new possibilities for spatial configuration.
Generative design, for example, uses AI to quickly produce multiple building design options based on specific constraints, optimizing both aesthetics and functionality. Additive manufacturing, utilizing materials such as self-healing concrete and climate-responsive glass, can reduce emissions and costs by up to 90%, while accelerating the production of prototypes and scale models. Furthermore, augmented and virtual reality technologies allow for the early detection of design and construction errors, while digital twins enable real-time monitoring and adjustments throughout the construction process.
4. Build

The physical construction of real estate spans the entire lifecycle—from planning and procurement to the building process and post-construction management. In MEA, construction faces persistent challenges, including manual project planning, fragmented performance management, opaque supply chains, and skilled labor shortages. These issues often result in cost and schedule overruns, further complicated by the growing demand for environmentally sustainable construction practices. However, digital innovations are beginning to penetrate this traditionally low-tech sector, with construction-related Proptech in MEA experiencing a 125% year-on-year increase from 2022 to 2023 in VC funding.
Construction management platforms now offer automated scheduling, performance tracking, and real-time communication, while procurement platforms streamline and increase transparency in the supply chain, improving efficiency for large projects. Prefabrication, which involves manufacturing building components off-site, significantly reduces errors and speeds up construction, cutting costs by 20% and reducing build times by up to 50%. Robotics further enhances efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, contributing to faster and more precise construction processes.
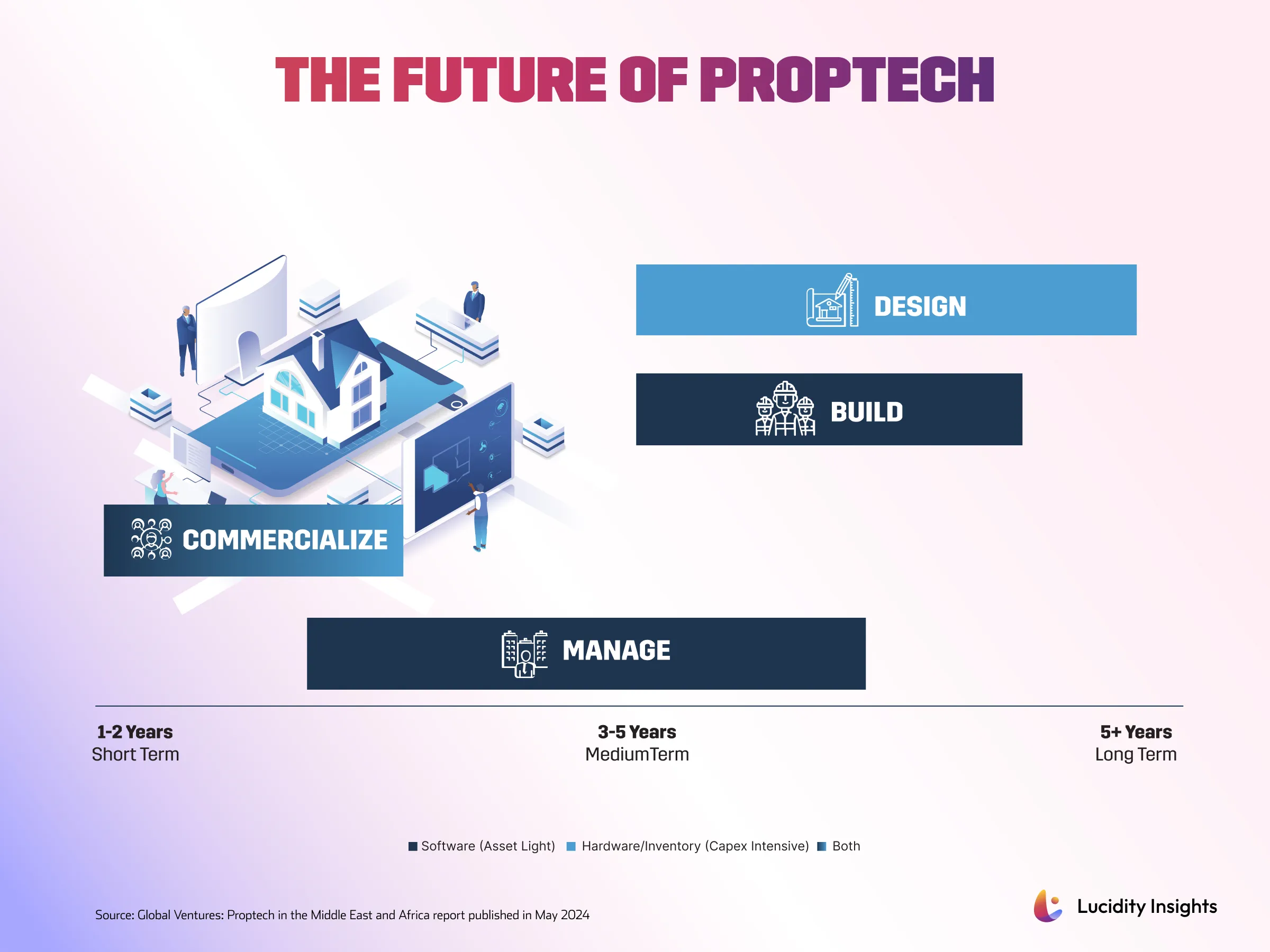
The Next 10 Years of Proptech in MEA

Many predict that the next decade will see a transformation across the Proptech value chain in MEA, presenting innovative solutions that streamline processes, boost sustainability, and improve affordability. The 4 key dimensions along the value chain will benefit each dimension in the following ways:
|
Design: |
Generative design, immersive experiences, additive manufacturing, 3D printing and material sciences |
|
Build: |
Construction management and procurement platforms, data-driven decision-making, modular construction, and robotics |
|
Commercialize: |
Marketplaces and fractional ownership
|
|
Manage: |
Co-working spaces, building and tenancy management, IoTs and service bundling
|
Investors Appetite for Proptech in the Middle East and Africa
In their report titled “Proptech in the Middle East and Africa”, Global Ventures highlights the significant growth and innovation in Venture Capital (VC) investment across the region’s Proptech sector. Between 2019 and 2023, MEA attracted an impressive US $778 million in VC funding for Proptech, with 85% of this investment concentrated in the GCC countries, underscoring the region’s pivotal role in driving technological advancements within the property market.

Also Read: Global Ventures: Pioneering Growth-Stage VC Investments in MENA


%2Fuploads%2Fproptech-2024%2Fcover25.jpg&w=3840&q=75)