Can Decentralized Identity (DID) Systems Built with Blockchain Help Us Say Goodbye to Identity Theft?
29 July 2024•
In the digital era, our lives are increasingly intertwined with a myriad of digital platforms, applications, and devices, weaving a complex web of data transactions that span the globe. This digital interconnectivity, while fostering unprecedented convenience and innovation, has also heightened the vulnerability of personal identity data.
Over the last two decades, this vulnerability has been starkly evidenced by the leakage of more than 16 billion identity records through data breaches and hacks, with a worrying trend showing that nearly 50% of these incidents occurred in the last five years. Notably, 6 out of every 10 stolen records are related to web services, technology platforms, and applications, underscoring the critical security challenges within these domains.
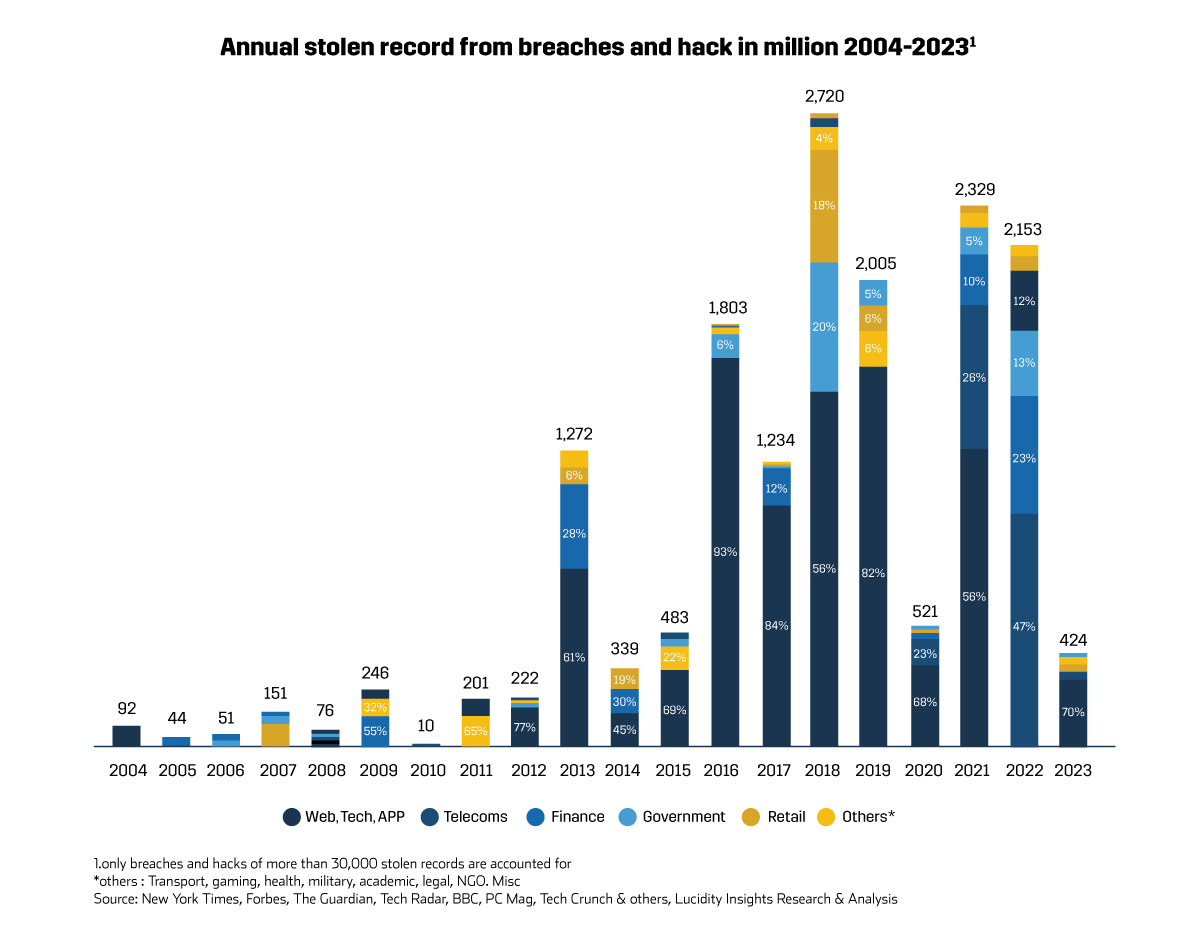
For instance, in 2021, LinkedIn experienced a significant breach where approximately 700 million users’ details were scraped using the official LinkedIn API, though, passwords were not compromised. Similarly, X (formerly Twitter) saw over 200 million users’ data, including emails and names, exposed from November 2022 to January 2023 due to repeated exploitations of security flaws, with the information subsequently posted on hacker forums.
In certain cases, data breaches have also led to the leakage of highly sensitive information. An illustrative example is the breach of India’s Aadhaar biometric database, a vast system holding the personal details of all registered Indian citizens. A security oversight at a state-owned utility company facilitated the unauthorized access to names, national identity numbers, and bank details, affecting approximately 550 million records. Disturbingly, this sensitive information was later found being sold on WhatsApp for less than £6.
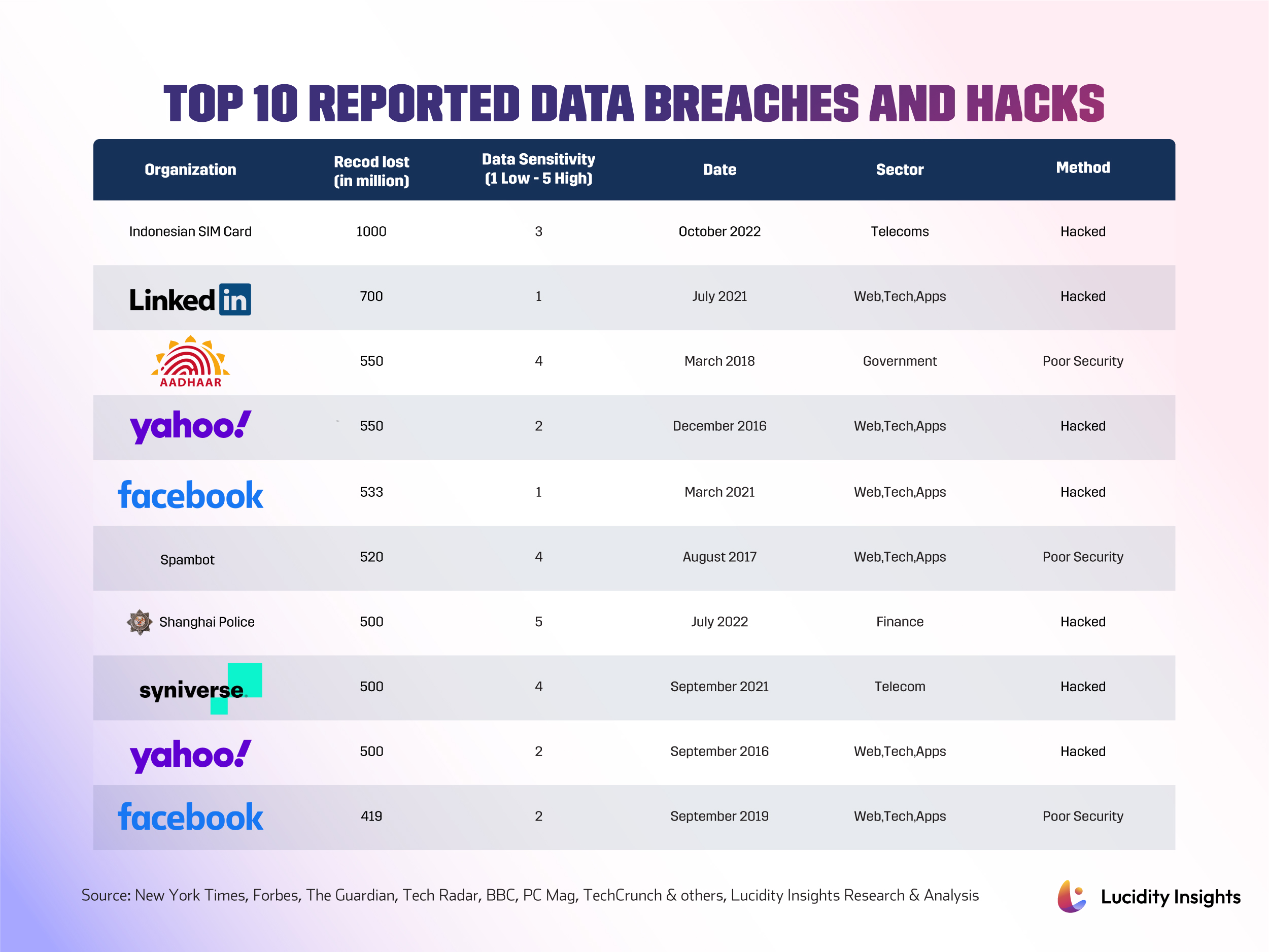 Infobyte: Top 10 Reported Data Breaches and Hacks
Infobyte: Top 10 Reported Data Breaches and Hacks
These incidents can have catastrophic effects, touching every aspect of our lives—social, professional, and financial. They can lead to severe consequences like identity theft, highlighting the need for a fundamental transformation in the way digital identities are managed and safeguarded. Blockchain technology, renowned for its promise of decentralization and superior security, emerges as a promising solution to these pressing challenges. Decentralized Identity (DID) systems propose a future where individuals have complete control over their personal data, marking the dawn of a new age in identity management characterized by enhanced security and user autonomy. This article delves into the existing state of identity management and the promising future offered by decentralized identities. It spotlights innovative projects leading the charge in transforming how we secure and administer digital identities in our increasingly digital and connected world.
Understanding Identity Management
At its core, identity is the unique information that defines a person, an entity, or an object. Imagine it as a personal signature, not just in the physical world where it might be your reputation or the mental notes people keep about you, but also in the digital world, where it gets a bit more structured. Here, your identity splits into two main parts:
- The Identifier: This is something distinctly yours, like a passport number or an Instagram handle. It’s a unique combination of characters or numbers assigned only to you.
- The Associated Data: These are the details that flesh out who you are in the digital realm—your travel history, your social media activities, and your academic or professional achievements.
Crafting a unified system for managing digital identities is complex. There’s no consensus on how it should be designed or operated, leading to a fragmented identity landscape. Our digital selves are often split across various platforms, controlled by a few dominant entities that guard this information to maintain their competitive edge.
This setup has significant implications:
- Companies view customer data as precious, often resisting efforts to share control over it.
- Industries like finance have specific requirements for managing digital interactions, complicating the creation of a universal system.
- Governments, controlling critical identifiers like driver’s licenses and passports, play a unique role in identity management.
Such a system creates a mismatch in power, limiting our control over our own data and hindering our ability to move seamlessly between online and offline worlds.\
Centralized Systems: A Double-Edged Sword
Centralized identity management systems are like giant digital ledgers kept by a single authority (think of a social media platform or a bank). They hold all the keys to vast amounts of personal data, from your birthdate to your transaction history. While they’ve been the standard for convenience and efficiency, they’re not without significant flaws:
- Privacy Concerns: Your data is at the mercy of the entity that controls it. How they use it, or who they might share it with, often goes beyond your control.
- Security Vulnerabilities: These systems are treasure troves for cybercriminals. A single breach can expose millions of users’ data in one fell swoop.
- Reliance on Third Parties: Ever forgotten a password? Then you know the drill of proving who you are to someone else who holds the keys to your digital kingdom.
As highlighted previously, identity theft is a growing concern in our digital society. Various mechanisms, including the Know Your Customer (KYC) standards, CAPTCHA Turing tests, and social trust graphs, have been implemented to counteract impersonation efforts. However, not all these measures safeguard privacy and anonymity. Often, they necessitate users to disclose personal identification details to certain entities, such as names, addresses, and passport numbers.
These shortcomings highlight the critical demand for innovative solutions in identity management. This is precisely where the concept of decentralized identity management emerges as a highly relevant and promising approach. This idea, predating even the cryptocurrency boom, aims to return control of personal data to individuals, moving away from the centralized gatekeepers. It’s driven by the recognition that the misuse of data and a growing distrust in large corporations necessitate a new approach to identity in the digital age.
Decentralized Identity (DID): A New Paradigm
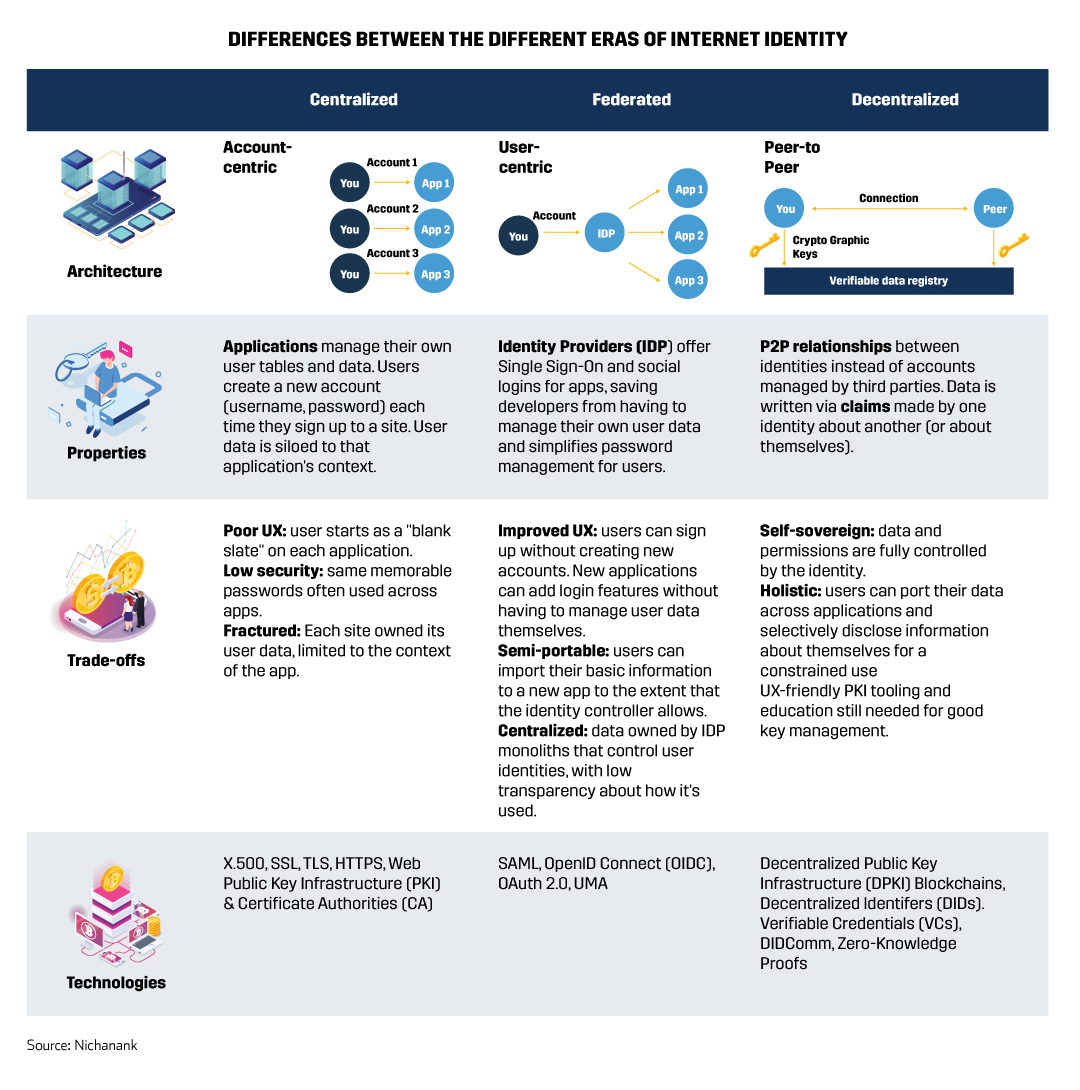
Decentralized Identity (DID) introduces a transformative approach to handling our online identities. Unlike traditional digital IDs stored on centralized servers, DIDs are securely anchored on blockchain technology, allowing individuals full control over their personal information. This method is akin to having a secure, digital vault that only you have the key to, dramatically enhancing privacy and security. DIDs and attestations are primary building blocks of decentralized identity where DIDs are issued and stored on non-centralized verifiable data registries (VDRs).
How DIDs Work
At its core, DID technology empowers users to generate their own digital identity independent of third parties. This identity is linked to a unique digital identifier that resides on a blockchain—a decentralized and secure digital ledger. Here, entities such as individuals, communities, and organizations can authenticate themselves, demonstrate ownership, and oversee their DIDs through a decentralized public key infrastructure (PKI).
This system diverges from the conventional web PKI by not depending on centralized certificate authorities (CAs) for its foundational trust. When you need to verify your identity, instead of submitting sensitive information directly, you use this unique identifier. Your identity details are securely stored on your device, and only you can decide which pieces of information to share and with whom, thanks to a set of cryptographic keys unique to your DID.
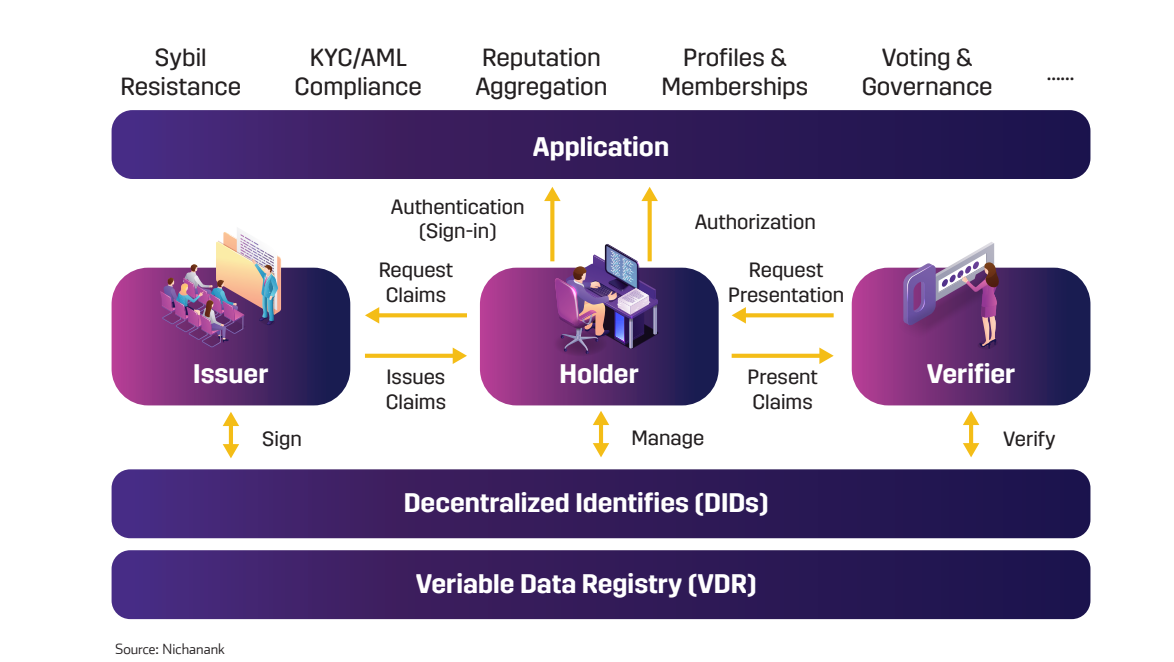
The Components of DID
DID operates on a straightforward model involving three key players: the issuer (who verifies the identity, like a government or educational institution), the verifier (who needs to confirm the identity, like a bank), and the identity owner (that’s you). This ecosystem ensures that your digital identity is both verifiable and under your control, sidestepping traditional security risks associated with centralized identity management.
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) possess four distinct characteristics:
- Decentralized: They operate independently of central authorities, allowing entities the freedom to establish an unlimited number of DIDs, tailored to specific contexts. This autonomy facilitates the management of various identities, personas, and interactions as desired.
- Persistent: Once a DID is assigned to an entity, it remains permanently linked to that entity. However, it’s worth noting that certain DIDs are designed to be temporary, catering to needs for ephemeral identities.
- Resolvable: DIDs enable the disclosure of further information about the entity they represent, allowing for a deeper understanding of the identity in question.
- Verifiable: The ownership of a DID or any claims associated with it can be authenticated directly by the entity, without the need for intermediary verification.
These fundamental attributes set DIDs apart from traditional identifiers like usernames, which lack verifiability; passports, which are not decentralized; and blockchain addresses, known for their nonpersistent nature and limited scope of resolvability.
The Advantages of Decentralized Identity
- User Empowerment: Users hold their identities, reducing dependence on central authorities and allowing them to decide what information to share and with whom.
- Enhanced Data Protection: By minimizing centralized points of failure, DIDs reduce the risk of identity theft and data breaches.
- Compliance with Privacy Regulations: DIDs help users and businesses meet stringent data privacy standards by providing a secure, verifiable KYC process.
- Prevention of Identity Fraud: DIDs help combat identity theft and fraudulent activities by providing a singular, immutable identity.
- Seamless Interoperability: DIDs facilitate the easy and secure sharing of information across various blockchain networks without the need for multiple identities.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain: The Backbone of DIDs
Blockchain technology, supported by cryptographic assets, plays a pivotal role in the DID ecosystem. It enables secure, decentralized transactions and identity management, with crypto assets offering additional security through cryptographic proofs, like zero-knowledge proofs. This decentralized framework ensures secure identity verification, control over personal data, and the elimination of intermediaries, paving the way for a more private and efficient digital world. Blockchains are just one layer of the web3 identity stack, which can be represented by the following categories:

The growing market of identity management and decentralized identity
 Infobyte: Decentralized Identity Market Size, by Region, 2018-2030 (USD Million)
Infobyte: Decentralized Identity Market Size, by Region, 2018-2030 (USD Million)
According to Polaris market research, the global decentralized identity market was valued at US $181.8 million in 2021 and is forecasted to reach US $46.5 billion by 2030 growing at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 89.1%.
Looking closer at the Web3 sector, CryptoRank found that since January 2022, projects in the “Digital Identity” field have raised over US $770 million, including almost US $40 million since January 2024. The market for Web3 identity is huge and complex, with many different projects addressing various use cases beyond just decentralized identity making it hard to track exactly how much money is being invested in the space. However, it is clear that the sector has captivated top-tier investors, including PayPal Ventures, Sequoia Capital, Andreessen Horowitz (A16z), Pantera Capital, Binance Ventures, and Coinbase Ventures, underscoring the robust investor confidence and the strategic importance placed on digital identity solutions.
The journey towards a fully realized decentralized identity ecosystem is marked by both challenges and transformative potential. As we navigate through the complexities of credential issuance, key management, and integration with existing web2 platforms, it’s clear that collaboration and innovation are key. The upcoming year promises significant strides in unifying disparate systems through mature aggregation layers, enhancing user experience, and expanding the utility of decentralized identities beyond the crypto realm.
Advancements in cryptographic tools and privacy preserving technologies are set to lay the groundwork for a next-generation identity infrastructure that is secure, accessible, and respects user privacy. As this megaproject unfolds, it’s evident that the collective effort of the entire ecosystem is crucial for success. The evolution of decentralized identity is not just about technological breakthroughs but about reimagining the very fabric of digital identity in our increasingly interconnected world.
To learn more about the innovations driving blockchain forward – read the full report here.

Related: Verax Redefining Trust in the Web3 Era: 8 Things That Happen When a Feature Becomes a Community Tool

%2Fuploads%2Finnovations-blockchain%2Fcover22.jpg&w=3840&q=75)